A letter of credit (LC) provides assurance to exporters that they will receive payment for their shipment even if the importer fails to make the payment. This reduces risks in international trade by ensuring the timely delivery of goods and payment to the exporter. However, the exporter still has to wait for the credit period to receive the payment.
To expedite this process, exporters can opt for LC discounting, where they receive immediate payment for the shipment from their bank. In this article, we’ll discuss the process of LC discounting, how to calculate it, and the typical charges associated with LC discounting in India.
What is LC-Backed Bill Discounting?
LC-backed bill discounting is a financing option provided by banks to exporters, specifically for export transactions supported by a letter of credit (LC). This facility allows exporters to receive immediate payment for their shipments, serving as a short-term credit solution to meet working capital needs.
Once the exporter and importer agree on the transaction and opt for an LC, the importer’s bank issues the LC. The exporter then submits the LC, along with required documents, to their bank. If all requirements are met, the exporter’s bank disburses payment to the exporter, deducting a discount from the bill of exchange amount.
LC-backed bill discounting enables exporters to receive prompt payment, while the importer benefits from an extended credit period, facilitating smoother trade transactions.
Features of LC Backed Bill Discounting in Exports
Here are some of the features of LC-backed Bill Discounting in Exports:
Assured Payment: LC-backed bill discounting provides exporters with assurance of payment by leveraging the letter of credit issued by the importer’s bank.
Export Working Capital: It serves as a short-term credit solution for exporters, offering immediate funds to meet working capital requirements.
Three Components: The process involves three main components – the letter of credit (LC), the bill representing the payment amount, and the discounting factor.
Requirement of LC: Banks offering LC bill discounting facilities require a copy of the LC issued to the importer by their bank, ensuring that the credit provided to the exporter is backed by the LC.
Payment Expectation: The bill outlines the amount expected by the exporter as payment for the shipment, facilitating clarity in financial transactions.
Discounting Factor: The discounting factor represents the fees deducted by the bank before disbursing payment to the exporter. These charges typically range between 6 percent and 15 percent of the total bill value.
Letter of Credit Discounting Charges: The discounting charges vary based on factors such as the credit period, invoice amount, and the creditworthiness of the buyer.
Bank’s Assurance: By offering LC-backed bill discounting, banks assure exporters of timely payment, enhancing trust and reliability in international trade transactions.
Payment Collection: At the end of the credit period, the bank collects the funds from the importer or the importer’s bank if they fail to complete the payment.
Flexible Financing: LC bill discounting provides exporters with flexibility in managing cash flow and fulfilling orders, supporting smooth trade operations.
Documents Required for LC Backed Bill Discounting
The following are the documents required to apply for LC bill discounting:
- Letter of credit from the importer
- Bill of exchange
- Commercial invoice and packing list
- Documents of title to goods evidencing the dispatch of goods or proof of delivery of goods
- Discounting request letter
- A bill of lading by the shipping line. Since LC discounting is almost always a type of post shipment finance service.
When Banks Can Decline to Provide LC-Backed Bill Discounting?
Banks play a crucial role in facilitating LC-backed bill discounting, a financial arrangement that provides exporters with immediate funds against the security of a letter of credit (LC). While this facility offers numerous benefits, including enhanced cash flow and reduced payment risk, banks may decline to provide LC-backed bill discounting for various reasons:
Document Authenticity
Banks meticulously review the documents submitted by exporters to ensure their genuineness. If any discrepancies or irregularities are detected, such as forged or misleading documents, the bank may refuse to proceed with the discounting facility.
‘Without Recourse’ Clause
Some financial institutions are reluctant to assume transactional risks associated with LC-backed bill discounting. If the letter of credit or bill of exchange includes a ‘without recourse’ clause, the exporter is absolved of responsibility if the importer fails to reimburse the paying bank. Banks may decline discounting in such scenarios due to heightened risk exposure.
Accommodation Bills
Discounting facilities are typically extended for genuine trade bills representing bona fide commercial transactions. However, if the submitted bills are deemed accommodation bills—drawn for mutual financial accommodation rather than actual trade—they may not meet the bank’s criteria for discounting.
Discrepancies in Documentation
Consistency and accuracy in documentation are paramount in international trade transactions. Banks may refuse discounting if discrepancies are observed between the descriptions of goods in the invoice and the bill of lading, indicating potential inconsistencies or inaccuracies in the transaction details.
Stale Bill of Lading
A bill of lading becomes stale if presented to the bank after the expiry date of the letter of credit. Banks may reject discounting if the bill of lading is not presented within the stipulated time frame, as it jeopardizes the validity and enforceability of the transaction.
Inadequate Insurance Coverage
Proper insurance coverage is essential to mitigate risks associated with the shipment of goods. If the exporter fails to provide evidence of adequate insurance for the transported goods, the bank may decline to proceed with discounting.
Revocable Letter of Credit
A revocable letter of credit grants the issuing bank the authority to modify or revoke the LC terms at any time without consent from the involved parties. Due to the inherent uncertainty and potential changes in payment terms, banks may be hesitant to discount revocable LCs.
Despite these potential challenges, financing institutions generally favor LC-backed bill discounting due to the security provided by the LC issued by the importer’s bank. However, exporters facing rejection can explore alternative financing options tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
How Does LC Backed Bill Discounting in Exports Works?
LC-backed bill discounting simplifies the transaction process between exporters and importers by leveraging the security provided by a letter of credit (LC). Here’s how the LC-backed bill discounting process works:
Sales Contract: The seller and buyer agree on a sales contract detailing the goods’ quantity, value, and terms of exchange.
Letter of Credit Issuance: At the seller’s request, the buyer approaches their bank (issuing bank) to issue a negotiable letter of credit (LC). This LC serves as a financial guarantee to the seller, assuring payment upon compliance with specified terms.
Transmission to Advising Bank: The issuing bank sends the LC to the advising bank, typically located in the seller’s jurisdiction. The advising bank verifies the authenticity of the LC and notifies the seller of its issuance.
Shipment and Document Submission: The seller ships the goods to the buyer and prepares the necessary export documents, including the bill of exchange, invoice, and shipping documents.
Document Verification: Upon receipt of export documents, the advising bank reviews them for compliance with the terms stipulated in the LC.
Communication with Issuing Bank: If the documents meet the LC requirements, the advising bank forwards them to the issuing bank for authentication.
Acceptance of Bill under LC: Upon verification, the issuing bank communicates its acceptance of the bill under the LC, confirming the seller’s compliance with contractual obligations.
Letter of Credit Transmission: The advising bank transmits the validated LC to the exporter, confirming its enforceability in the transaction.
Bill Discounting Application: Needing immediate funds, the exporter applies for bill discounting with the advising bank, leveraging the LC as collateral.
Discounting and Payment: The advising bank discounts the bill, deducting a fee known as letter of credit discounting charges, and advances the discounted amount to the exporter.
Payment Collection: On the due date specified in the LC, the advising bank collects the payment from the issuing bank, completing the transaction cycle.
Types of LC Backed Bill Discounting
Understand the different types of LC-backed bill discounting:
LC discounting charges comprise interest rates and processing fees, which vary based on factors like creditworthiness and duration of the discounting period.
Interest Rates
The primary component of LC discounting charges, interest rates, can range between 7% to 12-13% per annum in India, depending on the borrower’s credit profile. Longer discounting periods typically incur higher interest rates. For foreign bills, LC discounting rates are often linked to LIBOR rates, with an additional spread determined by the lender.
Processing Fee
Banks may levy a processing fee or bank handling fee in addition to interest rates. This fee is usually a flat amount or a small percentage (typically less than 2%) of the total discounting facility. The processing fee covers administrative costs associated with facilitating the LC discounting process and managing documentation.
Together, these charges contribute to the total cost of LC discounting, impacting the overall affordability and feasibility of utilizing this financing solution for exporters.
Also Read: Diverse Types of Export Letters of Credit
Calculating LC Backed Bill Discounting Charges
Discounting charges for LC-backed bills are determined using a straightforward formula: Discount charge = ((Funds in use x (Discount margin + Base Rate))/365) x number of days
Here’s a breakdown of the components and calculation:
Funds in Use: This refers to the total invoice amount submitted for discounting.
Base Rate: Unique to each bank, the base rate serves as a reference for calculating the discount charge.
Discount Margin: Typically expressed as a percentage over the base rate, the discount margin determines the additional charge applied.
For instance, let’s consider an example:
- Funds in use: INR 1,00,000
- Discount margin: 3% over the base rate
- Base rate: 3%
- Outstanding for 90 days
Using the formula:
- Discount charge = (((1,00,000 x (3% + 3%))/365) x 90
- Discount charge = INR 1479.45
By understanding this calculation, exporters can estimate the discounting charges associated with their LC-backed bills, aiding in financial planning and decision-making.
LC Backed Bill Discounting Limit
Banks and financial institutions offering various funding services, such as trade finance and working capital finance, may impose a threshold limit for discounting LC bills within a specified period. This limit, determined by the institution, is subject to variation and is contingent upon their discretion.
Also Read: LC at Sight: Meaning & Complete Process
Benefits of LC Backed Bill Discounting
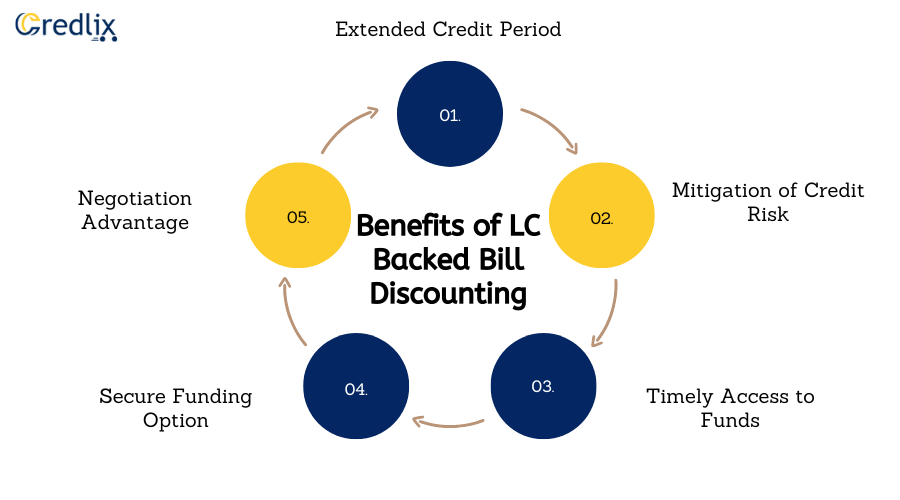
LC-backed bill discounting offers numerous advantages for both exporters and importers engaged in international trade transactions. Below are the key benefits of utilizing this financial instrument:
Extended Credit Period: Importers can benefit from a longer credit period provided by the letter of credit (LC), allowing them more time to complete the payment for the goods they have received. This extended credit period can help importers manage their cash flow more effectively and meet their financial obligations.
Mitigation of Credit Risk: For exporters, LC-backed bill discounting eliminates the risk of non-payment or delayed payment by the importer. The issuing bank’s assurance through the LC serves as a guarantee that the exporter will receive payment for the goods shipped, thereby reducing credit risk significantly.
Timely Access to Funds: By availing LC bill discounting, exporters can access funds before the due date mentioned in the LC. This early receipt of funds enables exporters to address immediate financial needs, such as financing production processes, investing in new projects, or settling payments to suppliers promptly.
Secure Funding Option: LC-backed bill discounting provides a secure and reliable source of financing for exporters. Banks only discount the LC after conducting thorough verification of the authenticity of the transaction and the creditworthiness of the parties involved. As a result, exporters can be assured of receiving funds in a timely and secure manner.
Negotiation Advantage: With the assurance of timely payment through LC-backed bill discounting, exporters can negotiate more favorable terms with their trading partners. The ability to offer longer credit payment terms enhances the exporter’s bargaining power and strengthens their relationship with importers, leading to more mutually beneficial trade agreements.
Non-Payment in LC Backed Bill Discounting
When the buyer fails to make payment for the discounted export bills, the repercussions are felt by both the exporter and the bank involved in the LC bill discounting transaction. Here’s what typically happens in such a scenario:
Debiting of Discounted Amount: The bank debits the discounted amount, along with any accrued interest charges, from the exporter’s account. This ensures that the bank recovers the funds it advanced to the exporter during the discounting process.
Potential Loss for the Exporter: The exporter suffers a financial loss due to non-payment by the buyer. Despite availing the LC-backed bill discounting facility, the exporter may still bear the brunt of the default if the buyer fails to fulfill their payment obligations.
Insurance Coverage: To mitigate the risk of non-payment, some banks may opt to obtain insurance against exporters. This insurance provides coverage against default of payments in LC bill discounting transactions, offering a level of financial protection to both the bank and the exporter.
Role of Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC): In India, the Export Credit Guarantee Corporation (ECGC) plays a crucial role in extending credit insurance coverage to banks and exporters. This coverage protects them against the risk of non-payment by buyers, safeguarding their financial interests in international trade transactions.
Overall, when the buyer fails to pay the discounted export bills, it can lead to financial losses for the exporter and the bank. However, measures such as insurance coverage provided by entities like ECGC help mitigate the risks associated with non-payment, offering a level of security to exporters and financial institutions involved in LC bill discounting transactions.
Also Read: Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC): Grasping Its Meaning, Varieties, and Operational Mechanism
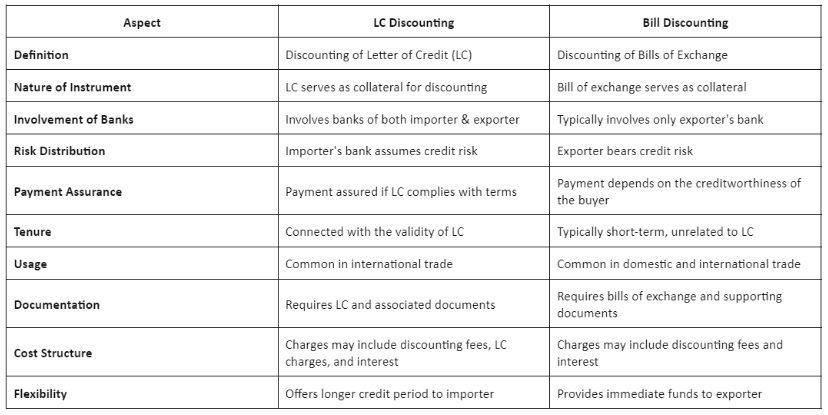
Difference Between LC Discounting and Bill Discounting
The table below provides an overview of the differences between LC discounting and bill discounting, covering various aspects such as nature, involvement of banks, risk distribution, payment assurance, tenure, usage, documentation, cost structure, and flexibility.
Conclusion
LC-backed bill discounting offers exporters immediate payment for their shipments, ensuring smoother trade transactions and mitigating payment risks. With the assurance of timely funds and extended credit periods, importers and exporters benefit from enhanced cash flow management and negotiation leverage. Despite potential challenges like document discrepancies, LC discounting remains a preferred financing option, fostering trust and reliability in international trade.
Also Read: The Intricacies of Back-to-Back Letters of Credit: A Comprehensive Overview




