
Quick Links:View All HSN Chapters |HSN Classification by Ministry
HSN Codes: What You Need to Know for Trade and Taxation
HSN codes, short for Harmonized System of Nomenclature, are like the universal language of trade and taxation. Whether you're an importer, exporter, manufacturer, or just curious about how goods get classified, understanding HSN codes is essential.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about HSN codes, from what they are and why they matter to how to find the right code for your product and the consequences of using the wrong one. Explore the world of HSN codes and discover how they simplify international trade and ensure accurate taxation.
Quick Facts About HSN Codes
- HSN Definition: HSN stands for Harmonized System of Nomenclature, a standardized international system for classifying goods.
- Global Standard: HSN codes are used worldwide to classify products for customs and taxation purposes.
- Digits in HSN: HSN codes typically consist of 6, 8, or 10 digits, depending on the level of detail needed.
- GST in India: In India, HSN codes are used under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system to categorize and tax goods.
- Tax Classification: HSN codes help determine the GST rate applicable to a product, ensuring accurate taxation.
- Uniform Reporting: HSN codes streamline trade and reporting, making it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations.
- Updates: The HSN system is periodically updated to reflect changes in global trade and product classification.
- Customs Declarations: HSN codes are crucial for customs declarations when importing or exporting goods.
- Trade Facilitation: They facilitate international trade by providing a common language for product classification.
- Specificity: The more digits in an HSN code, the more specific the product classification, providing detailed information about the item.
What Is HSN Code?
HSN stands for Harmonized System of Nomenclature. It's basically a system of codes used to classify and categorize products for trade and taxation purposes worldwide.
HSN code is a system of 6-digit codes that classifies over 5000 different products and is used worldwide. It was created by the World Customs Organization (WCO) and has been in use since 1988.
Imagine you have a big catalog of different items, like toys, electronics, clothes, and food. To make it easier for people and governments to understand and deal with these items, each one has a special code, like a secret number. This code tells everyone what the item is, where it comes from, and how it should be taxed.
So, HSN codes are like labels for products that help in organizing and managing them, especially when they're bought or sold internationally. They make it simpler to figure out what something is and how to handle it when it crosses borders or needs to be taxed.
Why Is HSN Important?
HSN helps organize and categorize products from all around the world in a structured way. This makes it easier to understand and trade goods internationally.
How Does the HSN Code System Function?
The HSN code system consists of 5,000 commodity groups, each with a unique six-digit code. These codes are organized logically and follow specific rules to ensure consistent classification.
Who Needs HSN Code?
- Importers and Exporters: HSN codes are essential for customs declarations during international trade.
- Manufacturers and Suppliers: They use HSN codes for precise product identification and invoicing.
- Tax Authorities: HSN codes aid in tax assessment and determining applicable rates.
- Businesses for GST: Under GST, businesses need HSN codes to file returns accurately.
- Regulatory Agencies: HSN codes help regulatory bodies monitor and control specific product categories.
- Logistics and Inventory Management: HSN codes streamline inventory management and logistics.
- International Trade Agreements: HSN codes facilitate standardized classification in trade agreements.
- Legal Compliance: Businesses use HSN codes to comply with product labeling and reporting requirements.
Who Provides HSN Code?
HSN codes are provided by an organization called DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade). They are like the managers of these codes. If there's a need to change or add new codes, or even get rid of old ones, DGFT takes care of it. They do this regularly to make sure the HSN codes are always up to date and accurate. It's all part of making the HSN code system work smoothly.
HSN Code Structure in India
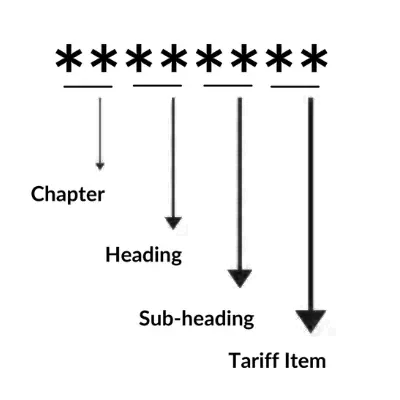
Understand The Concept of HSN Code
- The HSN structure has 21 sections, 99 chapters, 1,244 headings, and 5,224 subheadings.
- Sections and chapters categorize goods broadly, while headings and subheadings provide detailed descriptions.
- For example, "Handkerchiefs made of Textile matters 62.13.90" breaks down as:
- First two digits (62) stand for the chapter (Apparel and clothing accessories).
- Next two digits (13) indicate the heading (Handkerchiefs).
- Last two digits (90) represent the product (Textile handkerchiefs).
- India adds 2 more digits for deeper classification. If it's man-made fiber handkerchiefs, the code becomes 62.13.90.10.
HSN Codes With Examples
In simple terms, HSN codes are like product ID numbers. Depending on the size of your business and the type of product you're dealing with, you use either a 4, 6, or 8-digit HSN code. These codes help in accurately categorizing products for taxation and trade, whether you're selling locally or internationally.
Scenario 1:
Imagine Mr. A is a cement seller in India, and he needs to create invoices for his cement sales. His annual turnover is less than 5 crore rupees, so he needs to use a 4-digit HSN code. After some research, he finds out that the 4-digit HSN code 2521, which stands for "Cement, including cement clinkers," is the right code for his product. He includes this code in his invoices and GST returns.
Scenario 2:
Now, let's say Mr. A's business grows, and his turnover exceeds 5 crore rupees. In this case, he has to use a 6-digit HSN code. Since he sells aluminous cement, he finds the most accurate 6-digit HSN code for it, which is 252330.
Scenario 3:
Mr. A decides to export his cement to the USA. When dealing with international trade, he needs to be even more specific. For export transactions, he must use an 8-digit HSN code. Since he's exporting aluminous cement, he identifies the 8-digit HSN code as 25233000. He uses this code for his export documents and customs paperwork.
How HSN Codes Simplify International Trade and Taxation?
HSN codes provide a standardized way to classify and identify products, making international trade and taxation more efficient and less prone to errors.
Universal ClassificationHSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) is a global system that classifies products using a unique 6-digit code. This code is the same worldwide for the same product.
Detailed Descriptions: Each HSN code represents a specific product category. The first 2-4 digits provide a broader category, while all 6 digits together give a very detailed description of the product.
Customs and Trade: HSN codes are used primarily for customs and international trade. They help customs authorities understand what a product is and how it should be treated regarding taxes and regulations.
Taxation: In many countries, these codes are linked to tax rates. Different products have different tax rates, so HSN codes help determine the correct tax to apply.
Easy Identification: HSN codes make it easy to identify products when they cross borders. This simplifies the process of importing and exporting goods.
Regular Updates: HSN codes are updated periodically by organizations like DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade). This ensures that new products are accounted for, descriptions are accurate, and obsolete codes are removed.
Business Use: Businesses also use HSN codes for their internal record-keeping and reporting. It helps them classify their products accurately for various purposes, including tax compliance and inventory management.
International Trade Agreements: HSN codes play a crucial role in international trade agreements. They ensure that products are categorized uniformly, making it easier for countries to trade with each other.
What is Service Accounting Cost in GST
The Services Accounting Code (SAC) is a system of classification used in India's Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime to categorize different services for tax purposes. It helps in the systematic classification and taxation of services based on their characteristics. SAC codes are similar to the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN) codes used for goods.
Here's an explanation of SAC codes with an example:
Services Accounting Code Example:
SAC Code : 9983
Service Category : Business and Production Services
Description : Leasing or rental services without operator
In this example, let's say you run a car rental business. Your business falls under the "Leasing or rental services without operator" category, and the corresponding SAC code is 9983.
Here's how this works :
Categorization: SAC codes are divided into various categories, such as transportation, accommodation, telecommunications, financial services, etc. In this case, the service falls under the "Leasing or rental services without operator" category.
SAC Code: Each category has a specific SAC code associated with it. In this example, the SAC code is 9983, which is assigned to this particular category.
Taxation: When you provide car rental services, you will use SAC code 9983 on your invoices and GST returns. This code helps the GST authorities identify the type of service you are offering.
GST Rate: The GST rate applicable to your service will depend on its classification and SAC code. Different services may have different GST rates. You will charge and collect GST from your customers based on the applicable rate.
GST Filing: When you file your GST returns, you will report your revenue under the appropriate SAC code. This ensures that the government can accurately assess the GST liability for your service category.
It's important to use the correct SAC code for your specific service to ensure accurate taxation and compliance with GST regulations. Incorrect classification may lead to tax disputes and penalties.
You can find a comprehensive list of SAC codes and their descriptions in the official GST portal or consult with a tax professional to ensure you are using the correct code for your business.
Who Needs an HSN Code in GST?
Starting from April 1, 2021, the requirement for HSN codes in GST is based on your previous financial year's Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO):
Up to Rs. 5 crore AATO:
- Mandatory for B2B (business-to-business) tax invoices.
- Optional for B2C (business-to-consumer) tax invoices.
- The HSN code should have 4 digits.
More than Rs. 5 crore AATO:
- Mandatory for all invoices, whether B2B or B2C.
- The HSN code should have 6 digits.
So, your eligibility for an HSN code in GST depends on your annual turnover, and it's essential to use it correctly in your invoices based on these guidelines.
HSN Worldwide
The HSN system is like a universal language for more than 200 countries and economies. Here's why they use it:
Uniform Classification: HSN helps them classify things in the same way, making it easier to understand each other.
Customs Tariffs: It's the foundation for their customs tariffs, which are like taxes on things coming into or leaving a country.
Trade Stats: They use it to keep track of international trade, so they know what's going where.
In fact, almost everything traded internationally, over 98%, gets sorted using HSN. The HSN number for each item is usually the same for most countries. But in some places, it might be a little different, depending on the type of stuff they're dealing with.
HSN in India
India has been part of the World Customs Organization since 1971. They originally used 6-digit HSN codes to label things for customs and taxes. Later, they added two more digits to make the codes super precise, making it an 8-digit classification.
GST HSN Code Declaration Requirements
HSN codes for GST declaration until March 31, 2021:
| Turnover Range | HSN Digits Required |
|---|---|
| Up to 1.5 crore | No HSN digits |
| 1.5 crore - 5 crore | 2-digit HSN |
| More than 5 crore | 4-digit HSN |
Understanding HSN Code Declaration under GST
Starting April 1, 2021, businesses need to declare HSN codes on their GST invoices as per CGST notification 78/2020 dated October 15, 2020. The number of digits to declare depends on your annual turnover:
- Up to 5 crores: Mandatory 4-digit HSN for B2B invoices, optional for B2C.
- More than 5 crores: Mandatory 6-digit HSN for all invoices.
Make sure to use the turnover from the previous financial year (FY 2020-21 for FY 2021-22 invoices). This rule applies to every tax invoice under GST. For exports and imports, all 8 digits of the HSN code are mandatory.
Breakdown of the HSN Codes for Different Categories of Goods Chapter Wise
Chapter | Commodities |
Section I. Animals and Animal Products | |
Animals | |
Meat and edible offal | |
Fish, molluscs, crustaceans, and other aquatic invertebrates | |
Dairy produce, birds' eggs, honey and other edible products of animal origin that are not specified elsewhere | |
Other products of animal origin that are not specified elsewhere | |
Section II. Vegetables and Vegetable Products | |
Live trees and plants, bulbs, roots, etc., cut flowers and ornamental foliage | |
Edible vegetables, certain roots and tubers | |
Edible fruit and nuts, the peel of citrus fruits or melons | |
Tea, coffee, mate and spices | |
Cereals | |
Milling products, malt, wheat gluten, starches, and inulin | |
Oil seeds and oleaginous fruits, grains, straw and fodder, seeds and fruit, and industrial or medicinal plants | |
Lac, gum, resin, and other saps and extracts | |
Vegetable plaiting materials, and vegetable products that are not specified elsewhere | |
Section III. Animal or Vegetable Oils, Their Cleavage Products, Waxes, and Prepared Edible Fats | |
Animal or vegetable oils, their cleavage products, waxes, and prepared edible fats | |
Section IV. Prepared Food, Beverages, Spirits, Tobacco and Tobacco Substitutes | |
Preparation of meat, fish or crustaceans, molluscs, or any other aquatic invertebrates | |
Sugar and sugar confectionery | |
Cocoa and cocoa preparations | |
Preparations of cereals, starch, flour, milk, and pastry products | |
Preparation of vegetables, fruits, nuts, or plant parts | |
Miscellaneous edible preparations | |
Beverages, vinegar, and spirits | |
Residue and food waste, prepared animal fodder | |
Tobacco and tobacco substitutes that are manufactured | |
Section V. Minerals | |
Salt, earths and stones, sulphur, plastering material, lime, and cement | |
Ores, slag, and ash | |
Mineral fuel, mineral oils and products of their distillation, mineral waxes, and bituminous substances | |
Section VI. Chemical Products or of Allied Industries | |
Inorganic chemicals, organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals, rare-earth metals, radioactive elements, or isotopes | |
Organic chemicals | |
Pharmaceutical products | |
Fertilisers | |
Tanning or dyeing extracts, tannins and their derivatives, dyes, pigments, and other colouring matter, varnishes and paints, inks, putty and other mastics | |
Essential oils and resinoids, cosmetic or toilet preparations, perfumery | |
Soap, washing preparations, organic surface-active agents, lubricating preparations, prepared waxes, artificial waxes, polishing or scouring preparations, candles and similar items, modelling pastes, dental preparations and dental waxes with a basis of plaster | |
Albuminoidal substances, glues, enzymes, and modified starches | |
Explosives, pyrotechnic products, pyrophoric alloys, certain combustible preparations, and matches | |
Photographic or cinematographic goods | |
Miscellaneous chemical products | |
Section VII. Plastics, Rubber, and Articles Thereof | |
Plastics and plastic articles | |
Rubber and rubber articles | |
Section VIII. Raw Hides and Skins, Furskins and Articles Thereof, Leather, and Related Goods | |
Raw hides and skins (other than furskins) and leather | |
Articles made of leather, travel goods, handbags and similar containers, saddlery and harnesses, articles made of animal gut (other than silkworm gut) | |
Furskins and artificial fur and articles thereof | |
Section IX. Wood and Wooden Articles, Wood Charcoal, Cork and Articles of Cork, Basket Ware and Wickerwork, Manufacturers of Straw, Esparto or Other Plaiting Material | |
Wood and wooden articles, wood charcoal | |
Cork and articles of cork | |
Manufactures of straw, esparto or other plaiting materials, basket ware and wickerwork | |
Section X. Pulp of Wood or Other Fibrous Cellulosic Material, Recovered Paper or Paperboard (Waste and Scrap), Paper and Paperboard and Articles Thereof | |
Pulp of wood or other fibrous cellulosic material, recovered paper or paperboard (waste and scrap) | |
Paper and paperboard, articles made of paper pulp, or articles made of paper or paperboard. | |
Printed books, pictures, newspapers, and other products of the printing industry, typescripts, manuscripts, and plans | |
Section XI. Textile and Textile Articles | |
Silk | |
Wool, fine or coarse animal hair, horse hair yarn and other woven fabrics | |
Cotton | |
Other vegetable textile fibres, paper yarn and woven fabrics made of paper yarn | |
Man-made filaments | |
Man-made staple fibres | |
Wadding, felt and nonwovens, twine, cordage, special yarns, ropes, and cables and articles thereof | |
Carpets and textile floor coverings | |
Special woven fabrics, lace tapestries, tufted textile fabrics, trimmings, and embroidery | |
Impregnated, covered, coated, or laminated textile fabrics, textile articles made for industrial use. | |
Knitted or crocheted fabrics | |
Articles of apparel and clothing accessories that are knitted or crocheted | |
Articles of apparel and clothing accessories that are not knitted or crocheted | |
Other made up textile articles, sets, worn clothing and textile articles, and rags | |
Section XII. Footwear, Headgear, Umbrellas, Walking Sticks and Seat Sticks, Whips, Riding Crops and Parts Thereof, Artificial Flowers, Articles of Human Hair, Prepared Feathers and Articles Made Thereof | |
Footwear, gaiters, etc., and the parts of such articles | |
Headgear and parts thereof | |
Umbrellas and sun umbrellas, walking sticks, seat sticks, riding crops and parts thereof, and whips | |
Prepared feathers and down and articles made thereof, artificial flowers, and articles made of human hair | |
Section XIII. Articles Made of Stone, Plaster, Asbestos, Cement, Mica, or Other Similar Materials, Glass and Glassware, Ceramic Products | |
Articles made of stone, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica or similar materials | |
Ceramic products | |
Glass and glassware | |
Section XIV. Natural or Cultured Pearls, Precious Metals Clad With Precious Metal and Articles Thereof, Precious or Semi-Precious Stones, Coins, Imitation Jewellery | |
Natural or cultured pearls, precious metals, metals that are clad with precious metal and articles thereof, precious or semi-precious stones, imitation jewellery, coins | |
Section XV. Base Metal and Articles Made of Base Metal | |
Iron and steel | |
Articles made of iron or steel | |
Copper and articles thereof | |
Nickel and articles thereof | |
Aluminium and articles thereof | |
(Reserved for possible future use) | |
Lead and articles thereof | |
Zinc and articles thereof | |
Tin and articles thereof | |
Other base metals, cermets, and articles thereof | |
Tools, implements, spoons and forks, cutlery, of base metal, and parts thereof | |
Miscellaneous articles made of base metal | |
Section XVI. Machinery and Mechanical Appliances, Electrical Equipment and Parts Thereof, Sound Reproducers and Recorders, Television Image and Sound Reproducers and Recorders, and Parts and Accessories of Such Articles | |
Nuclear reactors, machinery and mechanical appliances, boilers, and parts thereof | |
Electrical machinery and equipment and parts thereof, sound reproducers and recorders, television image and sound reproducers and recorders, and parts and accessories of such articles | |
Section XVII. Vehicles, Aircraft, Vessels, and Associated Transport Equipment | |
Tramway or railway locomotives, tramway or railway track fixtures and fittings and parts thereof, rolling stock and parts thereof, mechanical (including electro-mechanical) traffic signalling equipment of all kinds | |
Vehicles other than tramway or railway rolling stock, and parts and accessories thereof | |
Aircraft, spacecrafts, and parts thereof | |
Ships, boats and floating structures | |
Section XVIII. Optical, Photographic, Cinematographic, Checking, Measuring, Precision, Medical or Surgical Instruments and Apparatus, Musical Instruments, Clocks and Watches, Parts and Accessories Thereof | |
Optical, photographic, cinematographic, checking, measuring, precision, medical or surgical instruments and apparatus, parts and accessories thereof | |
Clocks and watches and parts thereof | |
Musical instruments, and parts and accessories of such articles | |
Section XIX. Arms and Ammunition, Parts and Accessories Thereof | |
Arms and ammunition, parts and accessories thereof | |
Section XX. Miscellaneous Manufactured Articles | |
Furniture, mattresses, mattress supports, bedding, cushions and similar stuffed furnishing, lamps and lighting fittings, which are not elsewhere specified or included, illuminated signs and name-plates and the like, prefabricated buildings | |
Toys, games and sports requisites, parts and accessories thereof | |
Miscellaneous manufactured articles | |
Section XXI. Works of Art, Collectors’ Pieces and Antiques | |
Works of art, collectors' pieces and antiques | |
Project imports, laboratory chemicals, personal imports by air or post, passenger's baggage, ship stores | |
Services | |
These HSN codes help categorize and classify a wide range of products for international trade and taxation purposes, ensuring consistency and clarity in identifying goods.
How Do I Find My Product's HSN Code With an HSN Code Finder?
To find an HSN code using an HSN code finder, you can do it in a few easy ways:
Search by Product Name : Just type the name of your product, and you'll see suggestions for the most relevant 4-digit HSN codes. If the suggestions don't match, you can search for all results. Click on the 4-digit code to get more details, including the 6 and 8-digit codes for import-export and GST rates.
Search by HSN Code : If you already know part of the HSN code, type the first 2 or 4 digits. Click on the result you want to learn more about.
Use the Category List : HSN codes are sorted into 23 broad sections. You can navigate through these sections to find the 2-digit, 4-digit, 6-digit, and 8-digit HSN codes. To know the GST rates, click on the 4-digit code.
It's like searching for information about your product, and the HSN code finder helps you find the right code for it.
GST rates are directly linked to HSN codes. As announced at the 56th GST council meeting, new GST rates were implemented from 22nd September 2025. Businesses and individuals can check the latest GST rate changes here to understand how they impact products.
What are the Consequences of Using the Wrong HSN Code?
If you use the wrong HSN code as an exporter, it can cause trouble when your shipment goes through customs. You might face problems like not being allowed to import your goods, having to pay high customs taxes, or facing penalties for not following the rules.
In the case of GST (Goods and Services Tax), if you use the wrong HSN code, the buyer won't be able to get a tax credit. According to Section 31, an invoice must be accurate, including the right HSN code, for the buyer to claim a tax credit. So, using the correct code is really important to avoid these issues.
What Is The Difference Between ITC-HS Code And HSN Code?
The ITC-HS (Indian Trade Clarification-Harmonized System) code and HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code serve similar purposes but are used in different contexts.
The ITC-HS code is specific to India and is an extended version of the global HSN code. While both systems use a 6-digit structure for basic classification, the ITC-HS code further extends to 8 digits to provide more detailed product information. This extra precision helps Indian authorities in areas like customs, taxation, and trade statistics.
Essentially, the ITC-HS code is a country-specific adaptation of the HSN code, tailored to India's unique trade and regulatory needs.
How To Find Your Product in the HSN List and Its HSN Code?
To find your product's corresponding HSN code, use our convenient HSN Finder. It will help you identify the HSN code for goods and the SAC code for services effortlessly.
What is UQC and Its Connection with GST?
In the context of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India, "UQC" stands for "Unit Quantity Code." The UQC is a code used to specify the unit of measurement for goods and services. It is an essential component of the GST invoice format, as it helps in standardizing the reporting of quantities in various units.
The use of UQC ensures uniformity in describing the quantity of goods or services supplied in invoices, making it easier for both businesses and tax authorities to understand and process transactions accurately.
Examples of UQC codes include:
NOS: Stands for "Numbers." It is used when the quantity is counted in whole numbers, such as when selling items like pens or books.
KGS : Stands for "Kilograms." It is used when the quantity is measured in kilograms, commonly used for items like fruits, vegetables, or other products sold by weight.
LTR : Stands for "Liters." It is used for products sold in liquid form, such as beverages or oils.
MTR:Stands for "Meters." It is used for items sold by length, like cloth or cables.
By including the appropriate UQC in an invoice, businesses can accurately represent the quantity of goods or services being supplied, making it easier to calculate and apply GST correctly. This helps in GST compliance and reduces the chances of errors or disputes related to taxation.
FAQs
1. What is the full form of HSN?
HSN stands for "Harmonized System of Nomenclature," a global classification system for goods.
2. How to find HSN Code?
- Type your product name.
- Get recommendations for 4-digit HSN codes.
- If needed, search for all results for the right HS code.
3. Why Use 8-Digit HSN Codes?
The 8-digit HSN code is a unique identifier that provides detailed information about a product, including its GST rate. Each product has its distinct HSN code, simplifying classification and taxation. This system, known as the Harmonized System of Nomenclature (HSN), is developed by the World Customs Organization to streamline international trade
4. Where should HSN codes be mentioned?
HSN codes need to be mentioned on invoices, GST returns, and various official documents related to the sale and taxation of goods and services.
5. D/B HS and HSN Code?
HSN Code, or Harmonised System Nomenclature Code, is synonymous with HS Code in shipping. In India, it is commonly referred to as HSN. Both have six-digit codes for imports and exports.
6. Is a GST Bill Valid Without HSN Code?
No, a GST bill is not considered valid if it lacks an HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code.
7. Are HSN Codes Uniform Worldwide?
HSN codes are similar in countries under the World Customs Organisation (WCO), typically 6 digits. Some nations use 8-digit codes for further classification.
8. What Are SAC Codes?
SAC codes, or Service Accounting Codes, categorize services in India, much like HSN codes do for goods. They aid in GST taxation by assigning unique codes to service categories, ensuring accurate invoicing and tax reporting for services.
9. Are HSN Codes Required for Taxpayers Under the Composition Scheme or Dealing in Exempted Goods?
Taxpayers registered under the composition scheme and those dealing in exempted goods are also obligated to include HSN codes on their invoices, following the same guidelines as other registered businesses. This ensures uniformity in reporting goods for GST compliance.
10. How can I add an HSN code on the GST portal?
- Log in to GST PortaL
- Go to 'Services' > 'Registration' > 'Amendment of Registration Non-core fields.'
- Choose 'Goods and Services.'
- Click on 'Goods.'
- Enter the HSN code or item name.
- Save and continue.
- Verify and submit using DSC or EVC.
Disclaimer: Please note that the HSN code information provided has been obtained from the master codes published on the NIC's GST e-Invoice system. It is important to be aware that there may be variations in the codes due to government updates. Kindly acknowledge that we cannot be held responsible for any inaccuracies in the information provided.
65K +
Invoice Discounting
5000 +
MSMEs Onboarded
$350 mn+
Disbursed
120 +
Cities Coverage









