In 2024, global freight charges are estimated to reach over $1 trillion, highlighting the crucial role of shipping costs in international trade. Freight charges are the fees paid for transporting goods from one place to another, and they are a significant part of the total cost of trade. Understanding the HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code for freight charges helps businesses classify and manage these costs effectively.
The HSN code is a standardized system used to identify products and services in trade. Knowing the correct HSN code for freight charges ensures accurate billing and compliance with tax regulations. This guide will explain how to use the HSN code for freight charges in 2024.
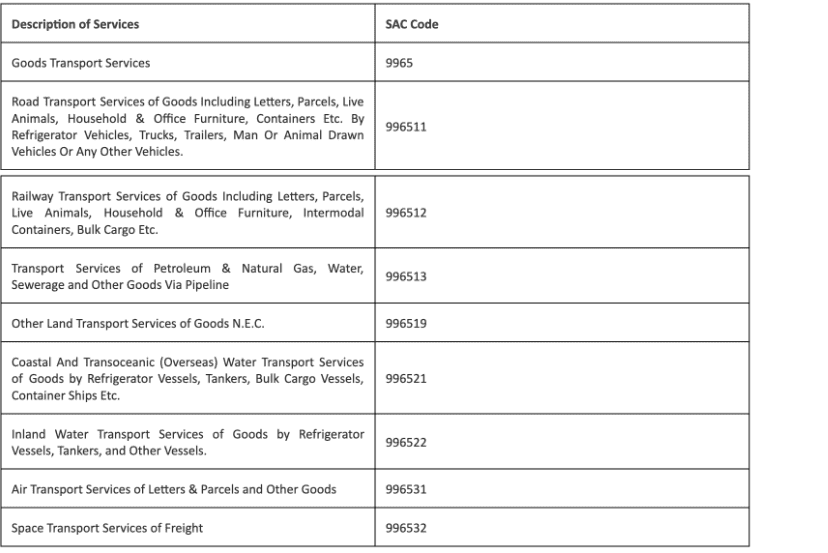
Freight and Good Transportation HSN Code/SAC
Here is the detailed table of SAC/ HSN Code for Freight and good transportation services of different nature:
Also Read: Freight Forwarding: Understanding the Vital Role of a Freight Forwarder
Types of Transportation Considered as Freight (According to GST)
Freight refers to the transportation of goods from one place to another. This can be done using different types of transportation. Here’s a simple breakdown of how freight is classified based on the mode of transport:
1. Land Transportation
- Goods Transport Services: This includes any transportation of goods, except consumable items, by land.
- Road Transport Services: Moving goods by trucks or lorries on roads.
- Railway Transport Services: Shipping goods by trains.
- Other Land Transport Services: This covers any other land-based transportation of goods not specified elsewhere.
2. Water Transportation
- Coastal and Transoceanic Shipping: Goods transported by ships across seas and oceans. This includes various types of vessels like bulk carriers, container ships, and tankers.
- Inland Waterways: Moving goods by boats or ships on rivers and lakes.
3. Pipeline Transportation
- Pipeline Transport: Moving goods like natural gas, petroleum, and water through pipelines.
4. Air Transportation
- Air Transport Services: Shipping goods by airplanes. This can include parcels, letters, and other items.
5. Space Transportation
- Space Transport Services: Transporting freight using spacecraft.
6. Freight Handling
- Freight Inward and Outward: Managing and processing goods coming in or going out.
- Freight Forwarding: Coordinating the movement of goods from one place to another.
- Shipping and Cargo Charges: Costs associated with shipping goods and handling cargo.
In summary, freight can be transported by land, water, air, or even space, and each method has its own specific services and charges.
What is Not Considered as Freight Under GST?
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, there are certain types of transportation that are not charged GST on freight. Here’s a simple list of what is excluded:
- Agricultural Produce: Transporting items like fruits, vegetables, and other farm products.
- Basic Food Items: Transportation of milk, salt, rice, flour, and pulses.
- Organic Manure: Transporting fertilizers made from natural materials.
- Newspapers and Magazines: Moving newspapers or magazines that are registered with the Registrar of Newspapers.
- Relief Materials: Transporting goods meant for helping people affected by natural or man-made disasters, accidents, or emergencies.
- Defence Equipment: Moving equipment used by the military or defense forces.
- Low-Cost Transportation: If the total cost of transporting goods in a single trip is less than Rs. 1,500.
In these cases, no GST is applied to the freight charges.
What Does Freight Charge Include and Exclude?
Freight charges are the costs you pay to move goods from one place to another. Here’s what these charges usually cover:
Includes:
Transportation Fees: The cost of actually moving your goods by truck, ship, plane, or train.
Handling Charges: Costs for loading and unloading your goods during transportation.
Insurance During Transit: Protection for your goods in case they are damaged or lost while being transported.
Excludes:
Customs Duties: Taxes you pay to government authorities when goods cross international borders.
Taxes: Additional taxes that may be applied to the cost of goods or services.
Fees at the Destination: Charges that may occur once your goods reach their final location, such as delivery or unpacking fees.
So, freight charges cover the basic costs of moving and handling your goods but don’t include duties, taxes, or any fees charged when the goods arrive at their destination.
Freight vs. Goods Transportation
“Freight” and “Goods Transportation Services” are two terms that often mean the same thing:
Freight: This term refers to the commercial moving of goods. It includes shipping cargo or merchandise from one place to another.
Goods Transportation Services: This term focuses on the services used to move goods. It highlights the organized process of transporting different types of products.
In simple terms, both terms are about moving items, but “freight” is the general term for the goods being transported, while “goods transportation services” describes the services and processes involved in moving those goods.
Conclusion
Understanding freight charges and their HSN codes is important for managing transportation costs and staying compliant with tax regulations. Freight refers to the cost of moving goods by land, water, air, or even space, and includes fees like transportation, handling, and insurance. However, it does not cover customs duties, taxes, or destination fees. Different types of transportation are classified under specific HSN codes, making it easier to identify and manage these costs. Certain transportation types are exempt from GST, such as agricultural produce and relief materials. Knowing these details helps businesses handle freight charges effectively and ensures smooth operations in trade.
Also Read: Difference between Freight Collect and Freight Prepaid: A Detailed Guide




