When engaging in international trade, businesses must navigate a variety of legal documents to ensure their goods move across borders without delay. One such crucial document is the commercial invoice. Whether you’re a seasoned exporter or a newcomer to global trade, understanding the importance of a commercial invoice and how to prepare it correctly can help you avoid costly delays and streamline your operations.
What is a Commercial Invoice?
A commercial invoice is a legal document used in international trade to process agreements between the exporter (seller) and importer (buyer). It serves as an official record that goods have been sold and shipped to the buyer. Unlike standard invoices used in local transactions, a commercial invoice is tailored for cross-border trade and is often accompanied by other shipping documents to facilitate customs clearance.
While there is no standardized format for a commercial invoice, it must include essential information such as the seller and buyer details, a description of the goods, shipment details, and the payment terms. Once the goods are shipped, the exporter issues this document to the importer, enabling both parties to have reliable terms of trade and facilitating customs clearance in both the export and import countries.
Why is a Commercial Invoice Important?
A commercial invoice serves multiple purposes in international trade, such as:
Facilitating Customs Clearance
Customs authorities in both the export and import countries require a commercial invoice to assess the value and nature of the goods being shipped. Without this document, customs clearance can be delayed, leading to fines or penalties.
Also Read: Customs Clearance Process: All the Steps an Exporter Needs to Follow
Record of Transaction
It provides a clear record of the transaction, including information about the buyer, seller, and the products being traded. This helps avoid disputes between the two parties and ensures smooth communication throughout the trade process.
Supporting Documentation for Payment
In international trade, banks, freight forwarders, customs brokers, and C&F (Clearing and Forwarding) agents often require a commercial invoice to process payments and release the goods. For instance, exporters shipping through FedEx or DHL must provide a FedEx or DHL commercial invoice to ensure that the shipment is properly processed.
When is a Commercial Invoice Required?
A commercial invoice is required for any international shipment carrying commercial value. It ensures compliance with the customs regulations of both the exporting and importing countries. The exporter prepares the document once the goods are ready to be shipped.
One important aspect of international commercial invoices is that they typically do not include taxes, as most international transactions are not subject to local taxes. Therefore, the exporter must ensure that all details are correct to prevent any issues during customs clearance.
Key Components of a Commercial Invoice
While there’s no fixed format for a commercial invoice, it must include specific details to meet the requirements of customs authorities and other involved parties. Below are the essential elements:
Exporter and Importer Information
Include the company names, addresses, and contact details of both the seller (exporter) and buyer (importer). If the buyer is not the consignee, you should provide the consignee’s details as well.
Shipment Details
Specify the mode of transport (air, sea, road, or rail), type of shipment (such as Full Container Load (FCL) or Less than Container Load (LCL)), and details of the containers used (e.g., reefer or insulated containers). Also, provide the vessel name, voyage number, and the ports of loading and discharge.
Product Information
Clearly describe the goods being shipped, including their quantity, weight, unit price, total price, and currency. You should also include classification codes such as the Harmonized System (HS) code or Schedule B codes, which help customs identify the products.
Payment and Trade Terms
Include the agreed payment method, terms of trade (such as Incoterms), and the name of the country where the goods originated. This section may also include details like the invoice number, shipping document references, and any relevant marine cover policy numbers.
Additional Information
To finalize the document, ensure that the name, date, and signature of an authorized representative from the exporter’s company are provided.
Creating a Commercial Invoice for International Shipping
Many shippers use templates in Microsoft Word or Excel to create invoices, but these can sometimes miss crucial information. Missing details can cause delays at customs, which could lead to extra costs. It can also confuse buyers or freight forwarders, resulting in fines or additional fees.
To avoid these issues, exporters might want to use export documentation tools like IncoDocs. These tools help you create accurate shipping documents, such as packing lists, and are often designed to follow international trade guidelines, making sure everything is compliant. This helps prevent shipment delays and ensures smooth trade processes.
The best solution is to use pre-filled online invoice forms. You can find these on websites like the UN Economic Commission for Europe (ECE) or through international shipping companies such as FedEx or UPS. Alternatively, you can download an invoice format from commercialinvoiceform.org, where you can directly enter your information online. The site even offers a glossary to explain terms on the form, making it easier to understand.
What Should a Commercial Invoice Include?
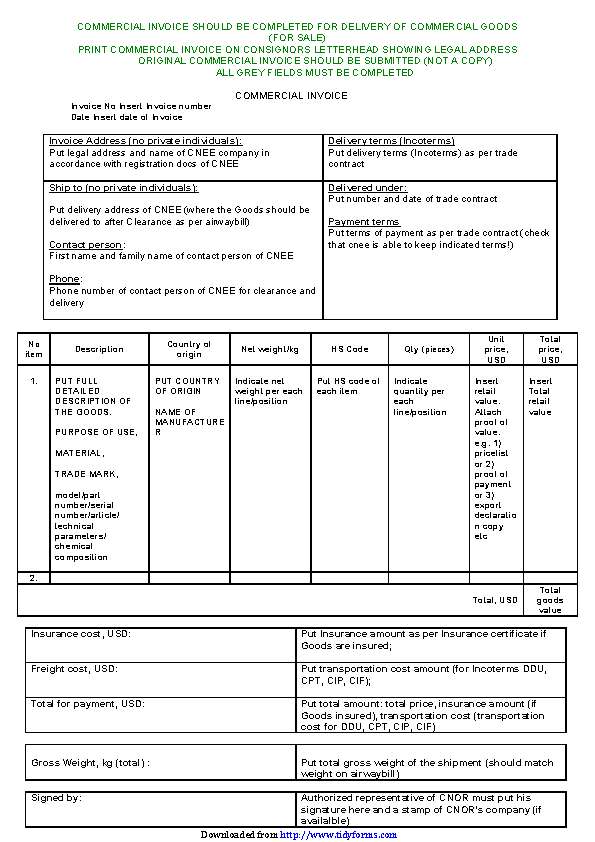
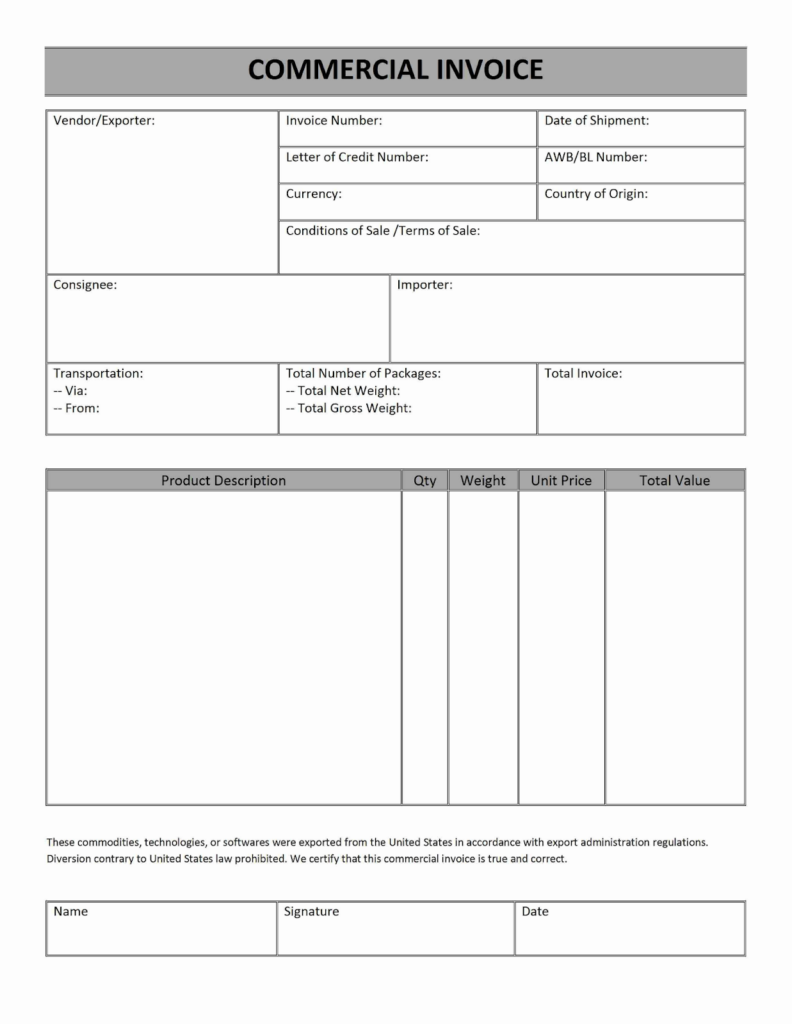
A commercial invoice is an important document in international trade. Here’s what you should include:
Details of the Goods:
- Description of the items
- Quantity
- Weight
- Price per unit and total value
Buyer and Seller Information:
- Full names
- Complete addresses
Payment and Delivery Terms:
- Payment method
- Delivery terms (Incoterms)
- Delivery time frame
- Country of origin of the goods
Mode of Transport:
- Air, sea, road, or rail
- Destination country
Identification Numbers:
- Tax ID number
- Exporter’s registration number
Additional Information:
- Invoice number and date
- Purchase order reference
- Harmonized System (HS) codes
- Any special instructions or certifications required
How to Fill Out a Commercial Invoice
There’s no fixed template for creating a commercial invoice, but it must contain all the key details about the transaction. When filling out the form, make sure to include information like tax ID numbers, addresses, and recipient details. If the buyer or seller is an individual, their tax ID might be their Social Security Number or an equivalent government-issued ID.
Lastly, for sections that don’t apply to your shipment, write ‘NA’ (Not Applicable) instead of leaving them blank. This ensures that the invoice is complete and won’t cause any confusion or delays.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When creating a commercial invoice, accuracy is crucial. Incorrect or missing information can lead to delays and fines. Some common mistakes include:
Missing Information: Ensure that all required fields are filled, including tax identification numbers, product classification codes, and payment terms. If certain fields are not applicable, fill them with “NA” rather than leaving them blank.
Using Non-Compliant Templates: While many exporters rely on templates created in Microsoft Word or Excel, these may not include all necessary information for international trade. To avoid delays, consider using specialized export documentation tools like IncoDocs, which align with the UN Layout Key recommendations for trade documentation.
Neglecting Trade Terms: Ensure that the terms of trade (such as Incoterms) are clearly outlined. This will help both the buyer and customs authorities understand the responsibilities of each party in the transaction.
Commercial Invoice vs Proforma Invoice
A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that outlines the terms of the sale before the shipment takes place. It provides an estimate of the transaction, including the price, quantity, and payment terms, but does not demand payment.
In contrast, a commercial invoice is issued after the goods have been shipped and provides a final record of the sale. It includes all details of the actual transaction, such as the payment amount, shipment method, and destination, and serves as a request for payment.
Commercial Invoice vs Tax Invoice
A tax invoice is issued for tax purposes, detailing the amount charged for goods or services, such as a GST invoice in India. It is primarily used for local transactions and is subject to local taxes.
A commercial invoice, on the other hand, is used for international transactions and outlines the terms of sale, product details, and shipping information. It may not include local taxes, as international shipments are often exempt.
Commercial Invoice vs Customs Invoice
While a commercial invoice is essential for international shipments, a customs invoice is a specialized version of the document required by customs authorities in the importing country. It includes additional information necessary for customs clearance, such as tariff classifications and duties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a commercial invoice have a zero value?
Yes, a commercial invoice can have a zero value if the goods are being shipped as samples or for demonstration purposes, with no charge to the buyer.
What is the difference between a commercial invoice and a packing list?
A commercial invoice is a legal statement detailing the transaction between the buyer and seller, while a packing list provides a breakdown of the goods being shipped. The packing list cannot replace the commercial invoice, but it is often used as a supporting document during shipping.
What is the difference between a commercial invoice and a certificate of origin?
A commercial invoice provides details of the sale, while a certificate of origin verifies the country where the goods were manufactured. Both documents are required for customs clearance, but they serve different purposes.
Conclusion
A commercial invoice plays a critical role in international trade, helping businesses maintain transparency, comply with customs regulations, and ensure smooth shipments. By understanding the essential components of this document and avoiding common mistakes, exporters can avoid delays, penalties, and ensure a hassle-free trade experience.
Also Read:




