Embarking on the journey of starting an export business is an exciting venture, filled with opportunities to connect with global markets and expand your horizons. However, the initial step often comes with a crucial question: how much finance is required to kickstart this endeavor?
In this blog, we will delve into the key financial considerations that budding exporters need to keep in mind. From market research and regulatory compliance to logistics, marketing, and managing potential risks, each aspect demands careful financial planning.
Join us as we navigate through the financial landscape of starting an export business, providing insights and tips to help you estimate the capital needed for a successful launch into the world of international trade. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a newcomer to the business world, understanding the financial requirements is a fundamental step towards building a robust foundation for your export venture.
Let’s explore the financial intricacies together and set the course for a successful and profitable export journey.
What are the Key Requirements To Start an Export Business?
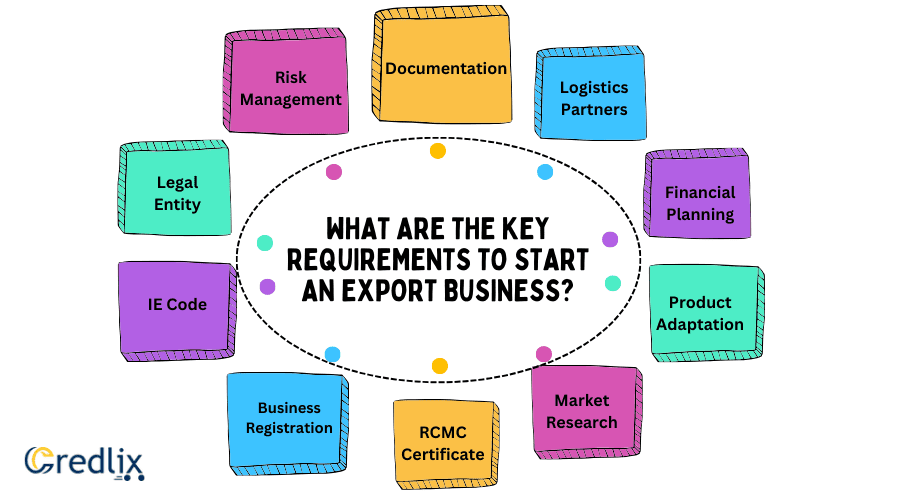
Here are some of the key requirements to start an export business in India:
Legal Entity
Establish a legal entity for your business, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or private limited company.
IE Code
Obtain an Import-Export Code (IE Code) from the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) in your country.
Business Registration
Register your business with the relevant authorities, ensuring compliance with local regulations.
RCMC Certificate
Obtain a Registration Cum Membership Certificate (RCMC) from the export promotion council.
Market Research
Conduct thorough market research to identify target markets, assess demand, and understand competition.
Product Adaptation
Customize your products to meet international standards and align with the preferences of the target market.
Financial Planning
Develop a comprehensive financial plan, including budgeting for initial investments and ongoing expenses.
Logistics Partners
Identify and collaborate with reliable freight forwarders and customs clearing agents for smooth transportation.
Documentation
Ensure proper documentation, including invoices, bills of lading, and certificates of origin, for smooth customs clearance.
Risk Management
Implement a robust risk management strategy, covering currency exchange, payment risks, and other potential challenges in international trade.
Key Expenses Areas in Launching Export Business
Starting an export business involves various expenses and investments. The major areas where money is typically utilized in the initial stages of an export business include:
Market Research: Understanding the target market is crucial. Money is spent on researching potential markets, identifying competitors, and analyzing market trends. This helps in making informed decisions and developing effective strategies.
Regulatory Compliance: Complying with international trade regulations is essential. Funds are required for obtaining necessary licenses, permits, and certifications to ensure legal and smooth export operations.
Product Adaptation: Adapting your product to meet the standards and preferences of the target market may be necessary. This could involve product modifications, packaging changes, or customization to align with local regulations and consumer preferences.
Marketing and Promotion: Promoting your products in the target market is vital. Money is spent on marketing strategies, advertising, creating promotional materials, and establishing an online presence. This could include participation in trade shows and industry events.
Logistics and Shipping: Exporting involves shipping goods to another country. Funds are needed for packaging, freight charges, shipping insurance, and other logistical expenses. Consideration should also be given to warehousing and distribution costs.
Documentation and Administration: Exporting requires accurate and comprehensive documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Money is utilized for preparing invoices, bills of lading, certificates of origin, and other required paperwork.
Legal and Professional Services: Seeking legal advice and hiring professionals such as customs brokers, freight forwarders, and export consultants can help navigate the complexities of international trade. Budget for legal fees and professional services.
Currency Exchange and Financial Management: Dealing with different currencies and managing foreign exchange risks is crucial. Funds may be allocated for currency conversion fees, hedging strategies, and international banking services.
Quality Control and Testing: Ensuring that your products meet the quality standards of the target market is essential. Money is invested in quality control measures, product testing, and certifications to gain trust and credibility.
Training and Education: Export staff may need training in international trade practices, regulations, and cultural awareness. Investing in employee education ensures a better understanding of the export process and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
Establishing Distribution Channels: Setting up effective distribution channels in the target market involves additional costs. This includes building relationships with distributors, retailers, and other partners.
Risk Management: Allocate funds for insurance against various risks, including transportation risks, currency fluctuations, and market-specific risks.
It’s important to create a comprehensive business plan that outlines these expenses and includes a financial projection to ensure that you have a clear understanding of the financial requirements for starting and sustaining your export business.
Financial Risks To Start an Export Business
While starting an export business, you may encounter the following financial risks. Understanding and actively managing these financial risks is essential for the long-term success and sustainability of an export business. Developing a comprehensive risk management strategy can help mitigate potential challenges and protect the financial health of the venture.
Currency Exchange Risk: Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the profitability of exported goods. Currency exchange risk arises when the value of the exporter’s currency changes unfavorably between the time of pricing and the actual transaction.
Payment Risks: Late payments or non-payment by international buyers pose financial risks. Exporters may face challenges in collecting payments due to differences in payment systems, creditworthiness issues, or disputes over product quality.
Market and Demand Volatility: Export businesses are exposed to market and demand uncertainties. Changes in consumer preferences, economic conditions, or geopolitical events in the target market can affect sales and revenue.
Political and Regulatory Risks: Political instability, changes in government policies, and regulatory uncertainties in the importing country can pose financial risks. Exporters need to navigate potential disruptions caused by political or regulatory changes.
Logistics and Transportation Risks: Challenges in the transportation and logistics chain, such as delays, damages, or theft of goods during transit, can impact the financial performance of an export business. Adequate insurance coverage is essential to mitigate these risks.
Credit and Financing Risks: Offering credit terms to international buyers introduces credit risk. Exporters may face challenges in assessing the creditworthiness of foreign customers, leading to potential losses due to payment defaults.
Cultural and Communication Risks: Miscommunication or cultural differences may lead to misunderstandings, affecting the successful completion of export transactions. This can result in financial losses and damage to business relationships.
Quality and Compliance Risks: Non-compliance with quality standards and regulations in the importing country can lead to financial losses through rejected shipments, legal penalties, and damage to the reputation of the export business.
Fluctuating Commodity Prices: Export businesses dealing in commodities may face risks associated with volatile commodity prices. Price fluctuations can impact profit margins and overall financial performance.
Intellectual Property Risks: Protecting intellectual property is crucial in international trade. Failure to safeguard patents, trademarks, and other intellectual assets can result in financial losses due to unauthorized use or infringement.
Economic Downturns: Economic downturns in the exporting or importing countries can lead to reduced demand for goods, affecting sales and revenue. Exporters need to be resilient to economic fluctuations.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Disruptions in the supply chain, such as shortages of raw materials or components, can impact production schedules and result in financial losses for export businesses.
Starting Your Import-Export Journey in India with Minimal Investment
Ever wondered if you can kickstart your import-export business in India without a hefty investment? The answer is yes! You don’t have to be a big player to tap into the lucrative foreign markets. Instead of diving into manufacturing or trading, consider being a sourcing agent or a middleman. By connecting manufacturers with international buyers, you can earn without massive upfront investments.
Starting small is another smart move. Begin with a modest supply, perhaps just $1000, to get a feel for the market. This approach allows you to test the waters and understand the dynamics before scaling up. Import-export doesn’t always demand substantial capital initially. As your business gains traction, you can gradually invest more, expanding your reach and boosting profits. Learn how to navigate the world of import-export business in India and maximize your returns without breaking the bank.
Cost for Securing your Import-Export License
For entrepreneurs with an existing firm or company, obtaining an import-export license involves a streamlined process. The key documents required for a swift issuance include your firm/company registration and two crucial certifications:
The Import-Export Code (IE Code) and the Registration Cum Membership Certificate (RCMC) from the export promotion council. These vital steps, while incurring costs in the range of a few thousand rupees, are the gateway to launching your Import-Export Service promptly.
Once your registration is complete, the next steps involve liaising with a reputable freight forwarder and customs clearing agent. Their expertise ensures seamless material transportation between countries, a pivotal aspect of international trade.
Navigating the setup of an import-export business in India typically incurs an initial investment ranging from Rs. 65,000 to Rs. 70,000. This investment lays the foundation for a compliant and efficient venture into the dynamic world of global trade.
Also Read: EXIM Policy of India: Meaning, Objectives, Functions, Features, Benefits
Strategic Ways to Optimize Your Initial Costs for Launching an Export Business
Embarking on an export business can be financially rewarding, but savvy entrepreneurs understand the importance of optimizing initial costs for long-term success. Here are key strategies to ensure your venture is cost-effective from the start:
Thorough Market Research
Invest time in comprehensive market research to identify target markets and assess demand. Understanding your audience enables focused and efficient spending.
Minimal Product Adaptation
Keep product adaptations to a minimum initially. Only make essential modifications to align with local regulations and preferences, reducing unnecessary expenses.
Digital Marketing and Online Presence
Leverage cost-effective digital marketing channels and establish a strong online presence. Utilize social media, content marketing, and search engine optimization to reach your audience without exorbitant advertising costs.
Freelance and Outsourcing
Consider outsourcing non-core functions such as design, content creation, and administrative tasks. Freelancers and outsourcing platforms can provide quality services at a fraction of the cost of in-house resources.
Efficient Logistics and Shipping
Negotiate competitive rates with logistics providers and shipping companies. Optimize packaging to minimize shipping costs while ensuring the safety of your products.
Utilize Government Incentives
Explore government programs and incentives that support export businesses. Many countries offer grants, subsidies, or tax breaks to encourage international trade.
Collaborate with Local Partners
Partnering with local distributors or agents can significantly reduce the need for heavy investments in establishing a foreign presence. Leverage existing networks to ease market entry.
Lean Operations
Keep operational costs in check by adopting lean practices. Efficient inventory management, streamlined processes, and prudent resource allocation contribute to cost optimization.
Negotiate Favorable Terms
Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, manufacturers, and service providers. Establish long-term relationships that may result in better pricing and terms.
Focus on Incremental Growth
Start with a small-scale operation to test the market and gradually scale up based on demand. Incremental growth allows you to manage and optimize costs effectively.
By implementing these strategies, aspiring exporters can launch their businesses with a keen eye on cost optimization, ensuring financial sustainability and long-term success in the global market.
Conclusion
Venturing into the world of export business requires a thoughtful approach to finances. From understanding the initial costs involved to navigating potential risks, we’ve explored key strategies for success. Whether you’re eyeing global markets or starting small in India, the key is to optimize costs wisely. Embrace digital avenues, leverage government incentives, and foster collaborative partnerships.
By focusing on incremental growth and efficient operations, you can build a resilient export business. Remember, it’s not about the size of your investment, but the smart decisions you make along the way that pave the path for a thriving and profitable journey into international trade.”




