Packing Credit plays a crucial role in facilitating smooth international trade for exporters by providing essential pre-shipment financing. Imagine you’re an exporter gearing up to send your products across borders. Before the actual shipment, there are numerous costs to cover, from procuring raw materials to packaging and transportation.
This is where Packing Credit steps in as a financial lifeline. It’s a short-term loan offered by financial institutions to exporters, allowing them to manage cash flow effectively and meet pre-export expenses.
This financial support ensures that businesses can fulfill export orders seamlessly without facing financial constraints. The credit is usually repaid once the exporter receives payment for the exported goods.
In essence, Packing Credit acts as the financial engine powering the journey of goods from production to shipment, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities of international trade with confidence.
What is Packing Credit In Export & What are Its Key Features?
Packing Credit is a type of short-term pre-shipment finance provided to exporters to meet their working capital needs before the actual shipment of goods. It is a loan or credit facility extended by financial institutions to exporters to help them with various pre-shipment expenses such as procuring raw materials, processing, packing, transportation, and other related activities.
The purpose of Packing Credit is to assist exporters in fulfilling their export orders without facing financial constraints. It allows exporters to manage their cash flow effectively and ensures the smooth execution of export orders.
Key features of Packing Credit in export:
Pre-shipment finance: Packing Credit is granted before the shipment of goods. It covers the period from the receipt of the export order to the shipment of the goods.
Nature of expenses: It covers various pre-shipment expenses such as procuring raw materials, processing, packing, transportation, warehousing, and other expenses related to the production and preparation of goods for export.
Short-term: Packing Credit is a short-term financing facility, and it is expected to be repaid once the exporter receives payment for the exported goods.
Collateral: Financial institutions may require collateral or security for providing Packing Credit, which can include assets, export documents, or a personal/corporate guarantee.
Interest rates: The interest rates for Packing Credit may vary and are typically competitive. The rates depend on factors such as the creditworthiness of the exporter, prevailing market conditions, and the terms negotiated with the financial institution.
Repayment: Repayment is expected to be made from the proceeds of the export bill. Once the exporter receives payment from the overseas buyer, they use the funds to repay the packing credit.
Packing Credit helps exporters manage cash flow, fulfill export orders, and ensures that the export process is carried out smoothly without financial constraints. It is an essential financial tool for businesses engaged in international trade.
Types of Packing Credit
Understand the different types of packing credit below:
Secured Shipping Loan: Secured Shipping Loan is a type of Packing Credit where the financing is specifically directed towards covering the costs associated with shipping and transporting the exported goods. This form of credit is secured against the shipment itself, providing the exporter with funds to manage transportation expenses, including freight charges and related costs.
Extended Packing Credit: Extended Packing Credit refers to an extended period of pre-shipment finance granted to exporters. It allows for a more extended repayment period, offering flexibility in managing pre-export expenses such as procurement, production, and packaging over a more extended time frame.
Advances Against Letter of Credit: This type involves obtaining financing by leveraging the Letter of Credit issued by the buyer’s bank. Financial institutions provide funds based on the security of the Letter of Credit, ensuring that the exporter has the necessary working capital to fulfill the export order.
Green or Red Letter of Credit: Green and Red Letters of Credit are variations indicating the status of compliance with specified terms. A “Green Letter of Credit” signifies compliance, while a “Red Letter of Credit” suggests discrepancies that need resolution before funds are released. The color coding simplifies the processing of export documents and payments.
Advances Against Duty Drawbacks: This involves obtaining credit against the duty drawbacks or refunds that exporters may be entitled to upon exporting goods. Duty drawbacks are incentives provided by the government to encourage exports, and exporters can leverage these as collateral for obtaining pre-shipment finance.
Pre-shipment Loan (Foreign Currency): Pre-shipment loans denominated in foreign currency assist exporters in managing expenses related to the production and preparation of goods for export. This type of credit is beneficial when dealing with international transactions, as it provides funds in the currency relevant to the export transaction.
Advances Against Export Incentives: Export incentives, such as government grants or subsidies, can be utilized as collateral to secure pre-shipment finance. This type of credit allows exporters to access funds based on the incentives they are entitled to receive upon completing the export.
Packing Credit Against Entitlements under Advance License (Imports): This involves obtaining packing credit based on the entitlements granted under an Advance License, which allows duty-free import of inputs for export production. Exporters can use this credit to cover pre-shipment expenses and later fulfill the export obligation as specified in the license.
Importance of Packing Credit?
In fostering economic growth, a nation’s export prowess is pivotal, prompting governments worldwide to champion and fortify their exporting community. Recognizing this, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) asserts that financial constraints should never be the stumbling block for international trade agreements. Enter Packing Credit—a financial tool instrumental in realizing this vision.
This credit facility empowers exporters by ensuring they have the requisite working capital to navigate the complexities of international trade. By availing Packing Credit, exporters can seamlessly meet pre-shipment expenses, spanning from procuring raw materials to packaging and transportation, enabling them to fulfill even the most substantial export orders.
In essence, Packing Credit acts as a catalyst, not only supporting businesses in executing export transactions but also contributing to the resilience and growth of a nation’s economy through sustained international trade success.
Eligibility Criteria for Export Packing Credit
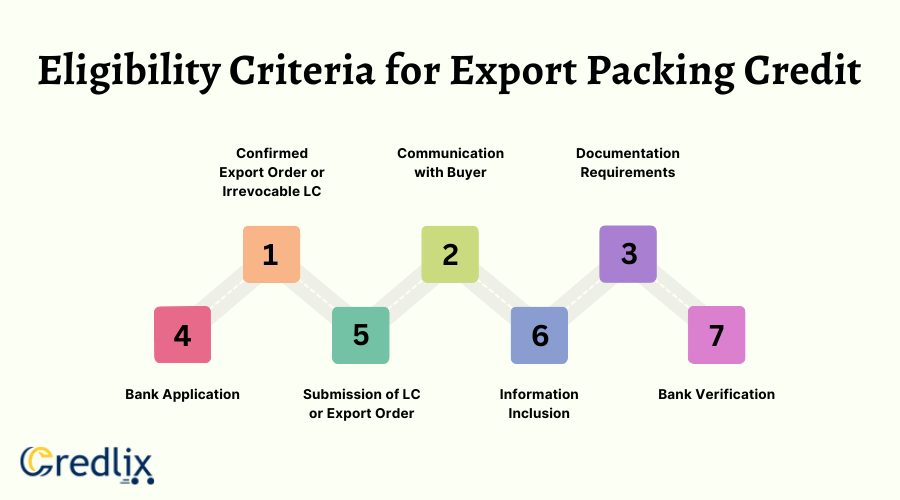
Check if you are eligible for Export Packing Credit below:
Confirmed Export Order or Irrevocable LC: Eligibility for Export Packing Credit requires an exporter to possess either a confirmed export order from a buyer or an irrevocable Letter of Credit (LC).
Communication with Buyer: In the absence of a confirmed order, the bank may consider providing packing credit based on documented communication between the exporter and the buyer. This communication should contain essential details like goods description, quantity, buyer’s information, etc.
Documentation Requirements:The communication used for eligibility should encompass crucial information, including a detailed description of goods, product quantity, and buyer’s particulars.
Bank Application: To avail of packing credit, the exporter must apply for the loan from any registered bank in the country.
Submission of LC or Export Order: Upon receiving the Letter of Credit or the export order at a later date, the exporter is required to submit these documents to the bank.
Information Inclusion: Any communication utilized for eligibility should incorporate vital details such as the nature of goods, quantity, buyer’s identity, and other pertinent information.
Bank Verification: The bank verifies the provided documentation, ensuring that it aligns with the necessary criteria before disbursing the packing credit.
Pre-shipment Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC)
Pre-shipment Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC) is like a special loan for exporters, given by the bank in a foreign currency. The exporter needs to pay back the loan in the same foreign currency, making it super convenient. This type of credit is great because it offers competitive interest rates globally, supporting exporters in their business.
However, there’s a catch. If the exporter doesn’t clear the PCFC loan within 360 days, it changes into a Rupee credit, and the interest rates shoot up until the full payment is made in Indian Rupees (INR). So, it’s like a time-bound benefit that keeps things affordable for exporters who settle the loan on time.
Obtaining Packing Credit: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s how you can obtain packing credit:
Initiate Application
Upon securing a confirmed export order, formally apply for packing credit by contacting your bank. Provide essential company documents along with details of the export order.
Document Verification
The bank assesses the credibility of the submitted documents. Based on this evaluation, they determine the credit amount. Typically, banks set a packing credit limit, often ranging from 20 to 25% of your total annual sales.
Order-specific Accounts
In cases of multiple export orders, distinct loan accounts are opened for each order. Once the credit is approved, the bank commences interest accrual until the complete repayment of the sanctioned amount.
Phased Disbursement
Banks may request information on your expenditure in phases, and they disburse the credit amount accordingly. This ensures a structured approach to utilizing the funds as needed.
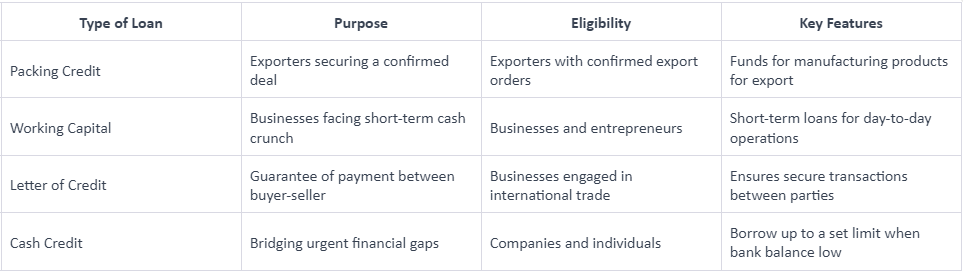
Packing Credit vs Working Capital vs Letter of Credit vs Cash Credit
Understand these four terms briefly below:
Packing Credit Example
Imagine you run a textile export business, and you just secured a confirmed order from an overseas buyer for a large shipment of premium fabrics. To fulfill this order, you’ll need to purchase raw materials, cover manufacturing costs, and arrange for transportation—all of which require significant upfront funds. Here’s where Packing Credit comes into play.
You approach your bank with the confirmed export order and apply for Packing Credit. The bank assesses the order’s legitimacy and your company’s creditworthiness. Once approved, they provide you with a short-term loan to cover the various pre-shipment expenses.
With the Packing Credit, you can now procure the necessary raw materials, pay for manufacturing processes, and arrange for the shipment of the textiles. This financial support ensures that your business can smoothly execute the export order without facing cash flow constraints.
Upon successfully delivering the textiles and receiving payment from the overseas buyer, you use the proceeds to repay the Packing Credit to the bank. In this way, Packing Credit acts as a crucial financial tool that enables exporters to fulfill international orders and contribute to the growth of their businesses.
Packing Credit for Deemed Exports
Packing Credit isn’t just for regular exports; it’s also extended to projects funded by global bodies like the World Bank. When materials are produced for these projects, they’re termed as deemed exports. For Packing Credit in Foreign Currency (PCFC), repayment for deemed exports is within 30 days or until payment by the funding agencies—whichever comes first.
However, despite its utility, Packing Credit has drawbacks. Exporters often find post-shipment finance more advantageous due to lower risks, quicker approvals, and lower interest rates, making it a preferable choice in many cases.
Final Words
In a nutshell, Packing Credit is the go-to financial support for exporters, ensuring they have the funds to kickstart the journey of their goods from production to shipment. From securing raw materials to covering shipping costs, it’s a crucial tool for meeting pre-export expenses.
However, with its time constraints and nuances, exporters often weigh alternatives like post-shipment finance for quicker approvals and lower risks. Nevertheless, Packing Credit remains a key player in fostering seamless international trade and supporting businesses in navigating the complexities of the global market.
FAQs
Who is eligible for availing packing credit?
Any Export House, Trading House, Star Trading House, Super Star Trading House, or exporter with a confirmed export order or letter of credit from the overseas buyer can avail packing credit.
Which institutions provide packing credit to exporters?
All registered banks extend packing credit facilities to exporters based on essential documents, such as a confirmed export order or an Irrevocable Letter of Credit.
How is the packing credit limit calculated?
Banks typically determine the packing credit limit as 20 to 25% of a company’s total annual sales when offering packing credit loans.
Can packing credit be liquidated?
Yes, packing credit is a self-liquidating credit, making it a reliable financial instrument.
What is the interest rate for packing credit?
Interest rates for packing credit vary among banks but generally fall between 4-5%, which is comparatively lower than rates for most other loans.
How does packing credit differ from post-shipment credit?
Packing credit is a pre-shipment finance, providing a loan against an export order before shipment. On the other hand, post-shipment credit is a loan against an already shipped export order.
Also Read: Comprehensive Guide on What is Post Shipment Credit to Exporters?




