When dealing with cross-border transactions, invoicing is a critical process that ensures the smooth flow of goods and payments. For exporters, understanding the nuances of different types of invoices, such as pro forma invoices and commercial invoices, is crucial to avoid delays, legal issues, or confusion. While both documents serve important roles in the transaction process, they differ significantly in their purpose, timing, and legal implications.
This guide will delve into the details of pro forma invoices and commercial invoices, their differences, and when to use each, making your invoicing process more efficient and error-free.
What Is a Pro Forma Invoice?
A pro forma invoice is essentially a quotation provided by the seller to the buyer before a transaction takes place. It is often referred to as a “good faith” document that outlines the terms of the sale without being legally binding. This document includes essential details such as:
- The price of the product or service
- The quality and quantity of goods
- Estimated taxes or transport charges
- Payment and delivery terms
Pro forma invoices are not requests for payment but rather a preview of what the buyer can expect. This allows the buyer to evaluate whether the transaction terms align with their expectations and budget.
When to Use a Pro Forma Invoice?
Pro forma invoices are typically used in the following situations:
Quotation for Approval: Companies use pro forma invoices to provide a formal quotation, especially when the buyer needs approval from internal departments before placing an order.
Customer Budgeting: Buyers can use pro forma invoices to assess the total costs, including estimated taxes, transport charges, and other applicable fees.
Customs Requirements: For international shipments, customs authorities may request a pro forma invoice before clearing the shipment for export.
Preliminary Negotiations: Sellers often issue a pro forma invoice to finalize the terms of the sale, ensuring transparency in pricing and delivery terms.
Key Features of a Pro Forma Invoice
Non-Binding Nature
A pro forma invoice is not a legally enforceable document. The buyer can choose not to proceed with the transaction even after receiving it.
Transparency
It helps create trust between the buyer and seller by clearly stating the terms of the sale upfront.
Standard Information
Details such as product description, HS code (for international shipments), estimated costs, and delivery terms are included.
Flexibility
The terms in a pro forma invoice can be adjusted before finalizing the sale, making it a dynamic document for negotiation.
What Is a Commercial Invoice?
A commercial invoice, unlike a pro forma invoice, is a legally binding document issued after the sale has been confirmed. It serves as a formal request for payment and is a crucial component in customs clearance for cross-border shipments.
The commercial invoice includes:
- Seller and buyer details (names, addresses, contact information)
- Description of goods (quality, quantity, and HS code)
- Payment terms and transaction currency
- Freight charges and mode of transportation
- Delivery destination
This document is essential for completing financial transactions and ensuring compliance with customs regulations.
Also Read: The Role of Commercial Invoices in Global Trade
When to Use a Commercial Invoice?
Commercial invoices are used in the following scenarios:
Payment Request
Once the buyer confirms the order, the commercial invoice is issued to request payment for the goods or services.
Customs Clearance
Customs authorities rely on the commercial invoice to determine the applicable duties and taxes. It is a mandatory document for clearing shipments.
Record-Keeping
Businesses use commercial invoices as part of their accounting records to track sales, payments, and inventory.
International Trade
In cross-border transactions, commercial invoices ensure both parties meet the regulatory requirements of exporting and importing countries.
Key Features of a Commercial Invoice
Legally Binding
Unlike a pro forma invoice, a commercial invoice is a legally enforceable document. Once issued, the buyer is obligated to pay according to the agreed terms.
Detailed Information
Commercial invoices provide comprehensive details about the shipment, including product HS codes, freight charges, and payment methods.
Customs Compliance
This invoice is critical for customs authorities to calculate taxes, duties, and verify the shipment against import regulations.
Proof of Sale
A commercial invoice confirms that a sale has occurred, making it an important document for both buyers and sellers to maintain in their records.
Pro Forma Invoice vs. Commercial Invoice: Key Differences
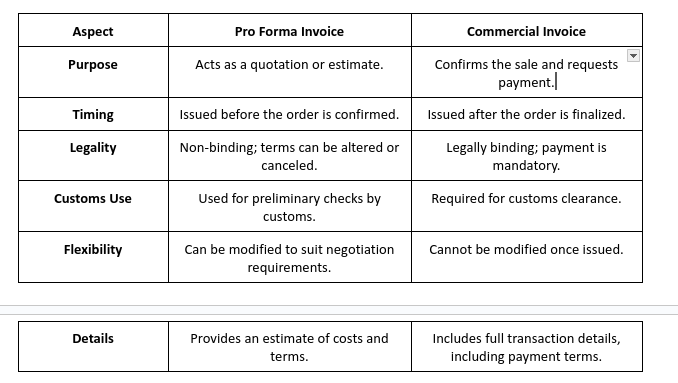
What You Need To Know About Proforma Invoice & Commercial Invoice
Proforma Invoice:
What are they?
A pro forma invoice is similar to a commercial invoice in almost all aspects. However, it provides the buyer with details about the product or service, which the seller is yet to deliver.
When are they issued?
A pro forma invoice is issued before the buyer places an order with the seller.
When are they accepted?
A pro forma invoice is accepted during the creation of the sale
What about entering in the book of accounts?
A pro-forma invoice isn’t a real invoice; it is only used for creating a sale. Hence, no entry is made in the book of accounts.
What are the objectives?
A pro forma invoice helps a buyer decide whether or not to place an order
Commercial Invoice:
What are they?
A commercial invoice, with details about the product or service, is sent to a buyer once the product/service has been delivered by the seller
When are they issued?
A commercial invoice is issued just before the payment has to be made.
When are they accepted?
A commercial invoice is accepted after the sale is confirmed.
What about entering in the book of accounts?
However, a commercial invoice is a real invoice that confirms the sale has occurred. Both, the buyer and seller can make an entry in the book of accounts based on the details provided in the commercial invoice.
What are the objectives?
A commercial invoice informs the buyer about the payment that is due.
Common Challenges Exporters Face
Exporters often find themselves confused about when to use a pro forma invoice versus a commercial invoice. This confusion can lead to various complications, including:
Delays in Customs Clearance: Using the wrong invoice can result in customs authorities holding the shipment for additional verification.
Disputes Over Payment: Issuing a commercial invoice prematurely may lead to payment disputes if the buyer hasn’t agreed to the terms.
Inaccurate Documentation: Errors in the invoice, such as incorrect HS codes or incomplete buyer details, can disrupt the transaction process.
Regulatory Non-Compliance: Different countries have specific requirements for commercial invoices. Failing to meet these standards can result in penalties.
Tips for Seamless Invoicing
To streamline the invoicing process and avoid potential challenges, follow these best practices:
Understand the Purpose: Clearly identify whether a pro forma invoice or a commercial invoice is needed for each transaction stage.
Double-Check Details: Ensure all information, such as product descriptions, HS codes, and buyer details, is accurate and complete.
Stay Updated on Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the invoicing requirements of the countries you’re exporting to.
Use Technology: Leverage invoicing software or tools to generate error-free invoices and maintain records systematically.
Communicate Clearly: Keep open communication with the buyer to ensure alignment on terms before issuing the final invoice.
Conclusion
Pro forma and commercial invoices are essential tools in the world of international trade, each serving a unique purpose. While the pro forma invoice facilitates preliminary discussions and approvals, the commercial invoice finalizes the transaction and ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Understanding the differences between these invoices, and knowing when to use each, can save you time, prevent costly mistakes, and foster trust with your trading partners. By following best practices and leveraging technology, you can simplify the invoicing process and focus on growing your business.
Also Read: Difference Between Commercial Invoice and Tax Invoice




