Expanding a successful business into new markets is a natural aspiration for entrepreneurs looking for continued growth and profitability. Venturing into overseas markets not only opens doors to potential higher profits but also provides insights into international demand for products and access to government incentives and subsidies. However, the allure of exporting is often dampened by the daunting procedures, extensive paperwork, and lack of clarity surrounding the process, which can overwhelm prospective exporters.
Despite the desire for a streamlined and hassle-free export process, the reality of foreign trade involves complex procedures and documentation, essential for managing foreign exchange transactions and mitigating risks such as fraud and black-market activities. Without proper documentation, it becomes challenging to assess critical aspects of the economy, including the current account balance. To support and encourage exporters, governments, such as that of India, have introduced initiatives like the Export-Oriented Units scheme (EOUs) and the Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) scheme, aimed at providing special incentives for exporters.
However, exporters are not exempt from the meticulous paperwork integral to the export business. This paperwork, while seemingly burdensome, serves as a crucial mechanism for ensuring transparency, accountability, and proper accounting of shipments. Two fundamental documents required for export transactions are the Export General Manifest (EGM) and the Shipping Bill, which are filed with the customs department. Understanding the significance of these documents and their differences is essential for navigating the complexities of international trade effectively.
What is the Export General Manifest?
The Export General Manifest (EGM) is a vital document in the realm of
international trade, serving as a comprehensive record of all cargo loaded onto a vessel destined for export. Filed by the carrier or their agent, the EGM plays a crucial role in facilitating customs clearance processes and ensuring transparency in the movement of goods across borders. It contains detailed information about the cargo, including descriptions, quantities, weights, packaging, and destination ports.
Essentially, the EGM serves as a critical link between exporters, carriers, and customs authorities, providing essential data for verifying the contents of shipments and ensuring compliance with export regulations. By documenting the cargo onboard a vessel, the EGM enables authorities to track and monitor exports, detect discrepancies, and prevent illicit activities such as smuggling. Its accuracy and completeness are paramount for the smooth flow of goods through international trade channels, making it an indispensable tool for exporters and regulatory agencies alike.
What is a Shipping Bill?
The Shipping Bill is a fundamental document in the realm of international trade, serving as a legal declaration submitted by exporters or their authorized representatives to customs authorities. This document is essential for obtaining clearance for exporting goods from one country to another. Filed before the actual shipment takes place, the Shipping Bill contains crucial details about the goods being exported, the exporter, the importer, and various aspects of the shipment.
As a comprehensive declaration, the Shipping Bill provides customs authorities with vital information necessary for processing and regulating exports. It includes details such as the exporter’s name and address, buyer’s information, description of goods, quantity, value, packaging, and any applicable export incentives or regulations. Additionally, the Shipping Bill plays a significant role in facilitating international trade by ensuring compliance with export laws and regulations of both the exporting and importing countries.
Furthermore, the Shipping Bill serves as a legal record of the export transaction, providing transparency and accountability in the movement of goods across borders. Its accurate and complete documentation is essential for customs clearance, enabling authorities to verify the legitimacy of exports and prevent illicit activities such as smuggling and trade fraud. In essence, the Shipping Bill is a critical component of the export process, enabling exporters to navigate regulatory requirements and facilitate the smooth flow of goods in the global marketplace.
Difference Between Export General Manifest and Shipping Bill
This elaborated table comparison should provide a comprehensive understanding of the distinctions between Export General Manifest (EGM) and Shipping Bill, covering various aspects such as submission, timing, content, responsibility, legal requirements, and associated documents.
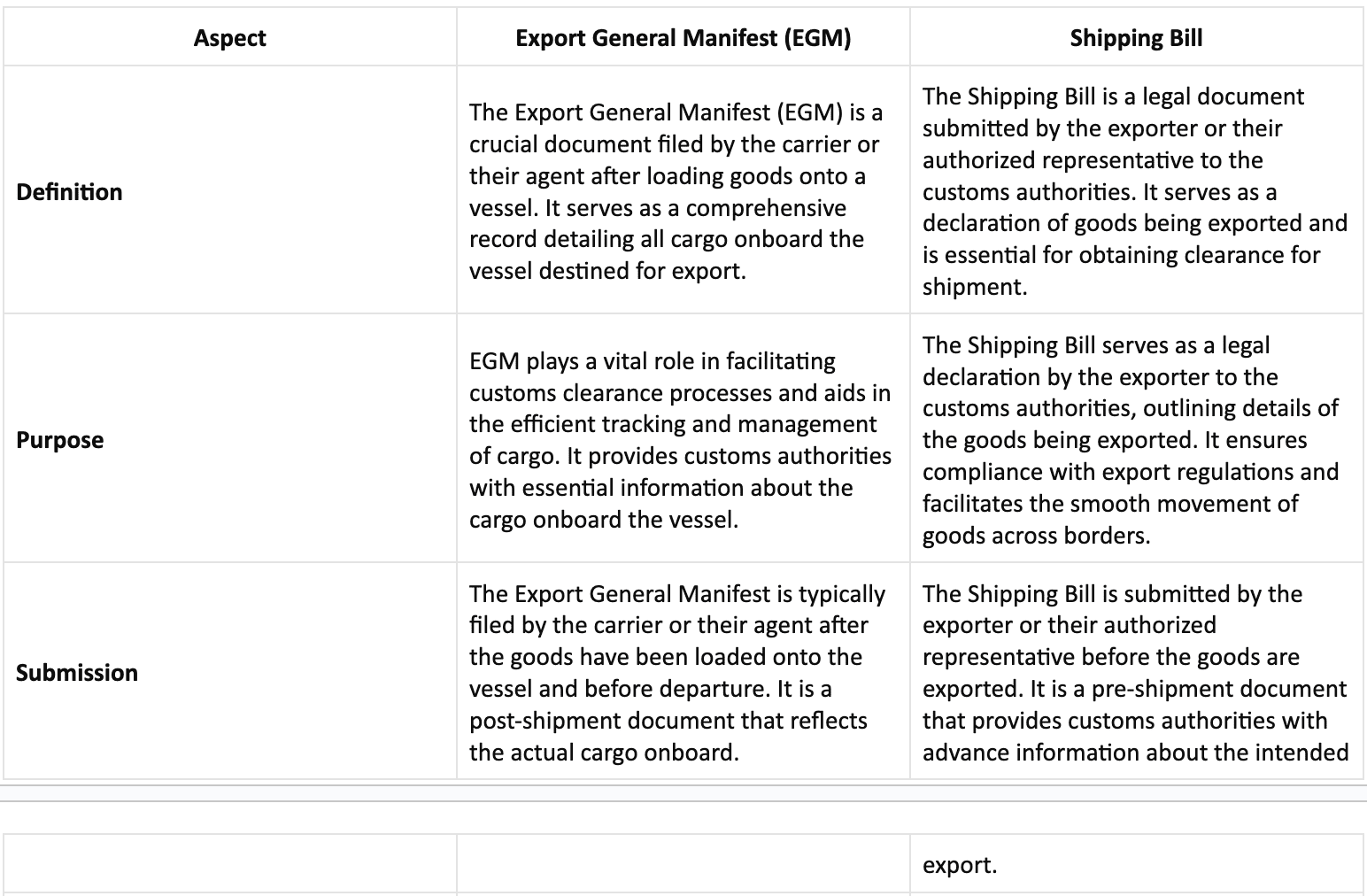
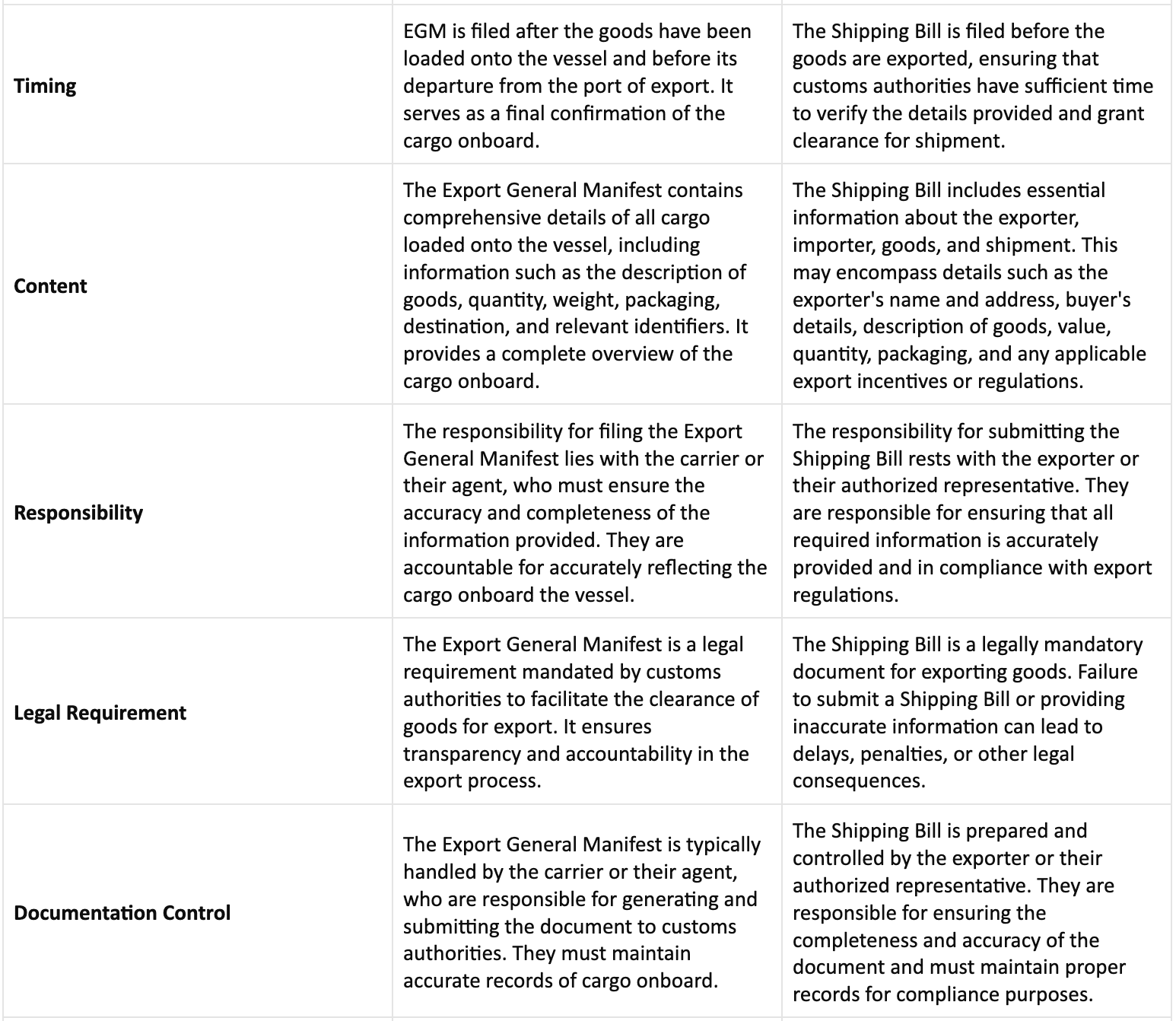



In conclusion, both the Export General Manifest (EGM) and Shipping Bill are important documents for making sure everything is clear and legal when exporting goods. The EGM lists all the items on the ship, helping customs, while the Shipping Bill is a formal declaration submitted by exporters. Even though dealing with paperwork can be tricky, following these steps is vital for ensuring smooth and honest trade between countries.
Also Read: How to Download Shipping Bills from ICEGATE?




