The GST system in India changed how businesses deal with taxes, and the HSN code plays a big role. aThis code helps classify goods and services in a standard way. Let’s talk about the HSN code for job work and why it matters in GST.
Basically, it helps businesses find the right category for their job work services. This makes things smoother for everyone involved. So, understanding and using the correct HSN code is essential for businesses operating under the GST system.
What is Job Work?
Job work is like asking someone else to do certain tasks for you. It could be things like making stuff, putting things together, or packing goods. For example, a company might hire another company to put their products together, and then the products come back to the original company, all ready to go.
In India, this is a big deal, especially for smaller and medium-sized companies. They send some parts of their work to other businesses called job workers, who are really good at those tasks. This helps smaller companies save money, work better, and focus on what they do best. It’s a win-win because job workers get to do what they’re good at, which creates jobs and helps the country grow.
So, job work is pretty important in India. It brings businesses together, helps them be more creative, and moves the country forward.
What is the HSN Code for Job Work?
The HSN code for job work is 9988. It is a crucial identifier for job work services in India. It covers a range of services related to job work, such as manufacturing for materials owned by others, processing goods on behalf of someone else, and providing printing or reproduction services under contract.
In the GST system, the tax rate for job work services depends on the rate applicable to the goods being worked on. For instance, if a job worker is crafting products from materials owned by a principal manufacturer, the GST rate will be determined by the HSN code rate for those final products.
Accurate classification with the right HSN code is vital to comply with GST regulations in India. It ensures proper tax calculation and helps avoid penalties. Each industry, be it textiles, jewelry, or leather, has its own specific HSN codes. Understanding how these codes operate for job work services is essential for businesses to stay compliant with GST rules, manage expenses effectively, and contribute to the country’s economic development.
Industry-Specific HSN Codes for Job Work Services in India
Different industries have their own specific HSN codes for job work services, alongside the general code 9988. Here are some examples:
Textile Industry – HSN Code 9987: This code is for services related to textiles, including weaving, knitting, sewing, and embroidery.
Jewellery Industry – HSN Code 9987: In the jewelry sector, the HSN code 9987 is used for services like cutting, polishing, and setting.
Printing Industry – HSN Code 9989: Services in the printing industry, such as printing newspapers, books, and journals, fall under HSN Code 9989.
These industry-specific HSN codes ensure accurate classification of services, ensuring compliance with GST regulations and appropriate tax rates for each sector.
Correct HSN Code for Job Work Services
Determining the appropriate HSN code for your job work services might seem like navigating through a maze. Fear not, as we’re here to provide you with a clear and straightforward roadmap:
Understanding Your Service: Let’s start with the basics. Take a moment to grasp the nature of your job work service. Are you engaged in manufacturing, processing, printing, or perhaps a combination of these activities? This initial understanding lays the foundation for further exploration.
Identifying Your Industry: Now, let’s consider the specific industry within which your services operate. Are you involved in textiles, jewelry, printing, or another sector altogether? This step is pivotal in narrowing down your search and tailoring your approach accordingly.
Consulting the HSN Code Book: Armed with insights into your service and industry, it’s time to turn to the HSN code book. Think of it as your trusty guide, containing a wealth of information on HSN codes and their corresponding definitions. Your goal here is to carefully match the characteristics of your service with the appropriate HSN code listed in the book.
Seeking Expert Assistance if Needed: If the process still seems daunting or if uncertainty persists, don’t hesitate to seek assistance from legal experts or tax consultants. These professionals can provide invaluable guidance, offering clarity and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
By following these steps diligently, you can navigate the intricacies of HSN code determination with ease. This not only facilitates accurate classification of your job work services but also ensures adherence to regulatory standards, ultimately contributing to the smooth operation of your business.
Sending Goods for Job Work under GST
If you’re registered under GST, you can send things like raw materials, equipment, or partially finished items to a job worker to get some work done. When you want these things back, you might have to pay GST on them, or in some cases, you might not need to pay any GST at all. It all depends on the situation.
Time Limits for Bringing Back Processed Goods under GST
When job work is done under GST, getting your goods back is important. You have two choices: bring them back to your place or send them directly to your customer, even for export. But there are time limits to remember.
For raw materials, you must either use them or get them back from the job worker within one year. For capital goods (except things like molds or fixtures), you have up to three years to bring them back. Time is crucial in managing your goods under GST. So, keep an eye on those deadlines!
Changes in GST Rates for Job Work Services
Learn about recent revisions to GST rates for job work services, including reductions for diamond-related job work and certain mechanical services. Discover how rates vary based on registration status and how these changes aim to simplify tax compliance for businesses.
GST Rate Changes for Job Work Services: The GST rates for job work services underwent revisions in a GST council meeting on September 20, 2019.
Diamond Job Work Services: The GST rate for job work services related to diamonds was reduced from 5% to 1.5%.
Mechanical Job Work Services: There was a reduction in the GST rate from 18% to 12% for mechanical job work services, particularly in the engineering industry. However, job work related to bus body construction still carries an 18% GST rate.
GST Rate Based on Registration: The GST rate depends on the registration status of both the job worker and the principal manufacturer. If both are registered, the GST rate is 12%. If only the job worker is registered, the rate is 18%. If neither is registered, there is no applicable rate (NA).
These changes aim to simplify the tax system, making it easier for businesses to understand and comply with the rules.
GST Procedures for Goods Sent to Job Work
Under GST, when sending goods for job work, it’s essential to include a challan to document the shipment. Goods must be retrieved within specific timeframes: one year for raw materials or finished goods, and three years for capital goods. Failure to do so may result in them being considered supplied to the job worker. Waste and scrap generated during the process have tax implications: if the job worker is registered, they handle taxes; if not, the responsibility falls on the principal who sent the goods. These procedures ensure clarity and tax compliance in managing goods and job work arrangements.
Easy GST Registration for Job Workers
Job workers must register for GST only if their yearly sales exceed a specific limit, regardless of whether their principal resides in the same state or elsewhere. However, those dealing with jewellery, gold, silverware, and similar items must register even if they provide services across state boundaries. This distinction ensures clarity and compliance for job workers under GST regulations.
Tax Liability in Job Work under GST
Under GST regulations, the tax liability for job work hinges on specific timelines. If goods are retrieved either six months before or within six months after the effective date, no tax is due. However, if retrieval occurs after this six-month window, tax payment becomes necessary.
Nonetheless, there’s a provision for an extension of this period by up to two additional months, offering some flexibility. This framework ensures that businesses engaging in job work activities adhere to tax regulations while allowing for reasonable adjustments based on operational needs. It’s crucial for businesses to track these timelines meticulously to manage their tax liabilities effectively and stay compliant with GST laws.
Input Tax Credit in Job Work under GST
Under the Input Tax Credit (ITC) provision in GST, when a principal sends inputs and capital goods to a job worker for processing, they are entitled to claim credit for the taxes paid on these items. What’s noteworthy is that this credit can be availed even if the goods are sent directly to the job worker without passing through the principal’s premises first.
In essence, the principal doesn’t need to wait for the goods to physically arrive at their own location to benefit from these tax advantages. This provision streamlines the process for principals engaging in job work activities, allowing them to promptly avail of tax credits and manage their tax liabilities efficiently. It promotes seamless business operations and compliance with GST regulations by facilitating the smooth flow of goods between principals and job workers.
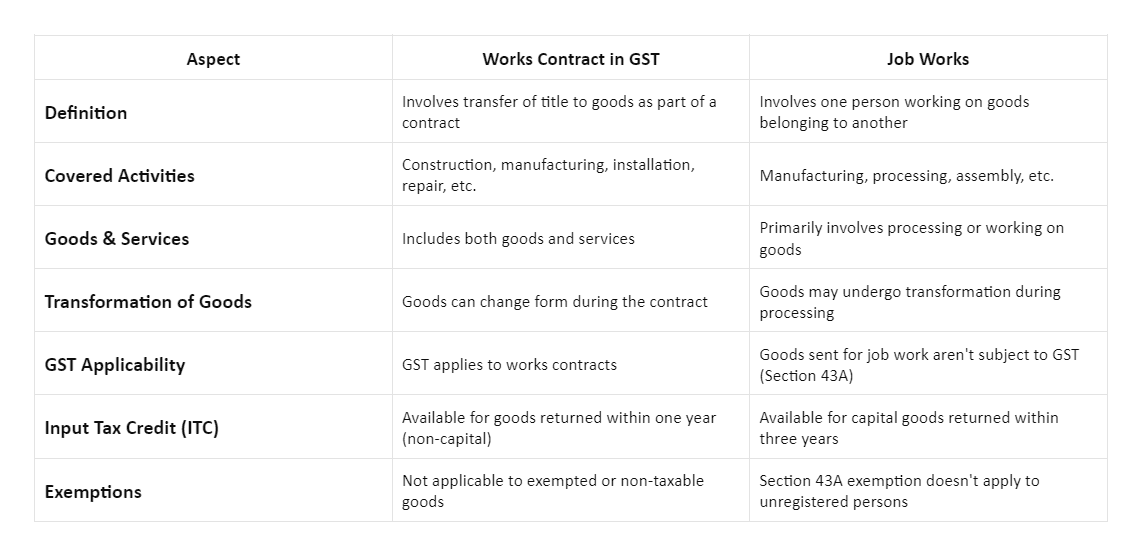
Difference between a Work Contract and Job Work
The table below provides a clear comparison between works contracts and job works under GST, covering aspects such as definition, covered activities, GST applicability, and input tax credit availability.
Quick Guide to Creating GST Invoices for Job Work
Learn how to create GST invoices for job work seamlessly with these quick and essential pointers. From preparing delivery challans to submitting necessary forms, ensure compliance and smooth operations in your job work processes.
- To send inputs or semi-finished goods to a job worker under GST, create a ‘Delivery Challan’.
- The challan should include the date and delivery challan number.
- Provide details such as name, address, and GSTIN of both the sender and recipient.
- Include HSN code, product details, and quantities.
- Specify CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST details separately, along with taxable value, tax rate, and tax amount.
- Don’t forget to mention the place of supply and include a signature.
- The information from the challan must be included in Form GSTR-1.
- Use Form GST ITC – 04 to provide challan details.
- Submit Form GST ITC – 04 quarterly by the 25th day of the month following the quarter.
- This process ensures compliance with GST regulations when dealing with job work.
In India’s GST system, the HSN code for job work services is crucial for accurate tax classification. Following the steps outlined in this article ensures businesses use the correct HSN code, maintaining compliance with GST rules and avoiding penalties. It’s about accuracy and adherence to the law.




