In the world of global trade, the journey from sending goods to receiving payments involves navigating a maze of financial intricacies known as post-shipment finance. For exporters, understanding this landscape is like having a compass in a dense forest – essential for reaching the destination of successful transactions. Let’s dive into the diverse types of post-shipment finance available to Indian exporters and discover how they can strategically harness these options to empower their trade endeavors.
Post-shipment finance serves as the vital link that connects the dispatching of goods to the receipt of payments. It encompasses a range of financial tools and strategies crafted to facilitate smooth trade across borders while minimizing risks and ensuring timely payments. Without a clear understanding of post-shipment finance, exporters may find themselves navigating choppy waters, struggling with cash flow management and transactional uncertainties.
In this journey, we embark on an exploration of post-shipment finance, with a focus on the plethora of options accessible to Indian exporters. By delving into these financial mechanisms, we aim to equip exporters with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate confidently and strengthen their foothold in the global market.
What is Post-Shipment Finance?
Post-shipment finance acts as a vital support system for exporters, providing them with the necessary financial resources after dispatching goods to international destinations, yet prior to receiving payment from buyers.
Think of it as a safety net, ensuring exporters can continue their operations seamlessly without being financially strained during the period between shipment and payment. It’s essential to recognize that various types of exports demand tailored financial solutions to effectively manage the financial aspects of their trade operations, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted flow of commerce.
Also Read: What Exporters Need to Know About Post-Shipment Credit
Varieties of Exports and Corresponding Financial Mechanisms
Physical Export
This category involves exporters whose names are explicitly stated in the trade documents. For physical exports, financial institutions extend credit or loans to facilitate the post-shipment phase, ensuring a smooth transition from sending goods to receiving payments.
Deemed Export
Under deemed exports, finance is provided to exporters supplying goods to domestic agencies. This financing mechanism is designed to streamline operations for exporters catering to domestic demand, ensuring they receive timely financial support.
Capital Goods and Project Export
In this segment, finance may be allocated in the name of the overseas buyer, with disbursement directed to the domestic exporter. This tailored approach simplifies financial transactions for large-scale capital goods and project exports, fostering smoother trade operations.
Popular Post-Shipment Finance Options
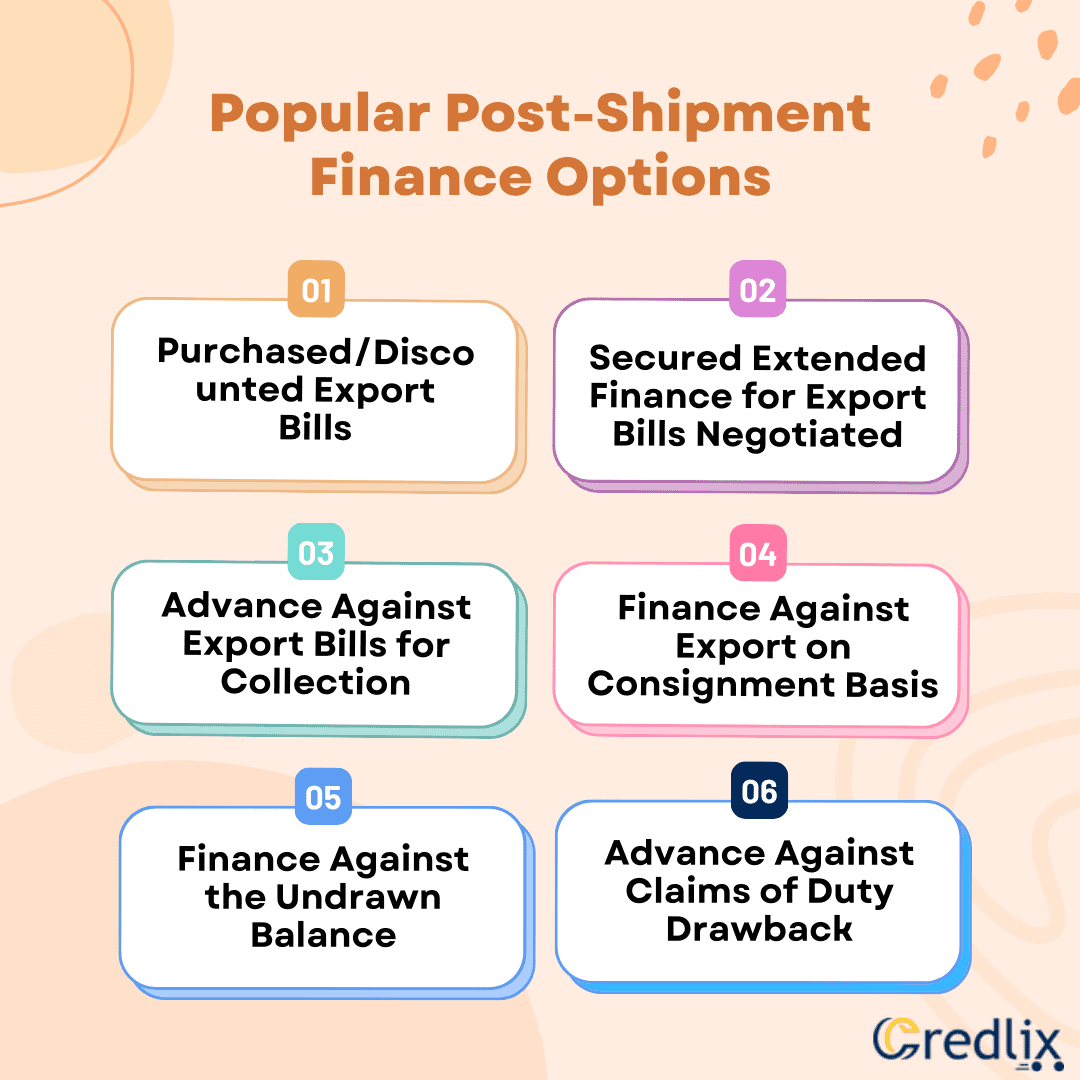
Here are some of the most popular post-shipment finance options available:
Purchased/Discounted Export Bills
Financial institutions extend specific limits to exporters to purchase or discount export bills, facilitating international trade transactions seamlessly by providing immediate access to funds. This option allows exporters to obtain cash upfront by selling their export receivables at a discounted rate, enabling them to meet immediate financial needs such as operating expenses, production costs, or fulfilling new orders.
By leveraging this option, exporters can optimize their cash flow and seize opportunities for business growth without having to wait for payment from buyers.
Secured Extended Finance for Export Bills Negotiated
Exporters benefit from reduced payment-related risks with banks extending finance for bills backed by letters of credit (LCs) and confirming LCs, ensuring guaranteed remittance and minimizing financial uncertainties. In this arrangement, banks provide financing against the security of confirmed export orders or LCs, mitigating the risk of non-payment by buyers.
By securing extended finance for negotiated export bills, exporters can confidently fulfill their contractual obligations, expand their business activities, and mitigate the impact of payment delays or defaults.
Advance Against Export Bills for Collection
Banks provide advances against collection bills in cases of discrepancies in LC bills, easing financial constraints for exporters until the realization of export proceeds, thereby enhancing cash flow management. This option enables exporters to access funds before the actual receipt of payment by providing documentation of the export transaction.
By availing advances against export bills for collection, exporters can bridge the gap between shipment and payment, ensuring smooth operations and timely fulfillment of financial obligations.
Finance Against Export on Consignment Basis
Banks offer financing when goods are sent on consignment, mitigating risks for exporters by ensuring timely payments from consignees and safeguarding against potential losses. This arrangement allows exporters to obtain financing against the value of goods sent on consignment, providing them with the necessary liquidity to cover production costs, overheads, or other expenses.
By accessing finance against export on a consignment basis, exporters can mitigate the risk of non-payment or delayed payment from consignees, thereby reducing financial uncertainty and ensuring a steady cash flow.
Finance Against the Undrawn Balance
Exporters can access finance against the undrawn balance, enabling effective management of complexities in international trade transactions and optimizing cash flow dynamics. This option allows exporters to leverage their unused credit limits or unutilized balances under export contracts to obtain financing from banks.
By accessing finance against the undrawn balance, exporters can enhance liquidity, seize business opportunities, and mitigate financial risks associated with fluctuating market conditions or unforeseen expenses.
Advance Against Claims of Duty Drawback
Banks provide advances against duty drawback claims, supporting exporters in global markets by offering financial assistance based on eligibility criteria, thereby enhancing liquidity and operational flexibility. This option enables exporters to obtain funds against anticipated duty drawback benefits, allowing them to address immediate financial needs or invest in business expansion initiatives.
By availing advances against claims of duty drawback, exporters can optimize cash flow, improve working capital management, and capitalize on export incentives provided by government authorities.
Also Read: What are the Post-Shipment Banking Activities in the Export Business?
The Crystallization of Overdue Export Bills
The “Crystallization of Overdue Export Bills” arises when payments for exports are not received by the stipulated due date. In such instances, the outstanding export bills are converted into liabilities denominated in the exporter’s domestic currency, often in rupees. This underscores the critical need to expedite the collection of export proceeds to mitigate financial risks effectively.
By converting foreign exchange into local currency liabilities, this process reflects the financial loss incurred due to delayed or non-payment. Prompt action to realize export proceeds becomes imperative to maintain financial stability and liquidity, safeguarding the exporter’s interests and ensuring the smooth functioning of trade operations.
Conclusion
These diverse post-shipment finance options serve as indispensable tools for exporters navigating the multifaceted terrain of international trade. It is paramount for exporters to remain abreast of evolving regulations and financial mechanisms to optimize their operations effectively and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the global marketplace.
By leveraging a comprehensive understanding of post-shipment finance, exporters can enhance their competitiveness, mitigate risks, and foster sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected world economy.
Also Read: Role of Post Shipment Credit in Facilitating International Trade