Some goods, not listed in the US Munitions List (USML) or the Commodity Control List (CCL), fall under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). Known as EAR99, exporters typically don’t need a license to ship these items in most situations. Despite their classification, EAR99 items still require compliance with export regulations and may be subject to specific restrictions or controls.
EAR99 designation encompasses a wide range of products, making it important for exporters to understand and navigate applicable regulations to ensure lawful and smooth international trade transactions.
What Does EAR99 Mean?
EAR99 stands for “Export Administration Regulations 99.” It denotes products that can be exported from the US or re-exported globally without the need for a license. Typically comprising low-tech consumer goods and services, EAR99 items are subject to supervision by the US Department of Commerce. While they may not require a license, caution is needed to ensure they aren’t exported to embargoed countries, supplied to prohibited users, or used unlawfully. Compliance with export regulations remains essential to ensure lawful trade practices and prevent misuse of EAR99 products.
Requirements and Compliance of EAR99
EAR99 regulations govern the export of products that don’t fall under the US Munitions List (USML) or the Commodity Control List (CCL). Here’s a breakdown of key regulations:
- Export Flexibility: EAR99 products can typically be exported to other countries without significant restrictions, as long as their end-use is lawful and not prohibited.
- Export to Restricted Countries: If the intended export destination is a country subject to US sanctions or embargoes, exporters may need to obtain a license to proceed with the export.
- ECCN Assignment: Export Control Classification Numbers (ECCNs) categorize products based on various factors like tangibility, performance characteristics, and end-use. Since EAR99 items are not listed in the CCL, they do not have an assigned ECCN.
Adherence to EAR99 regulations is crucial to ensure compliance with US export laws and regulations, prevent unauthorized exports, and maintain national security interests.
Benefits of Using EAR99 Products in Export
EAR99 products offer several advantages for exporters, making them a popular choice for international trade. Here’s why they are worth considering:
Simplified Regulation: With an EAR99 classification, products are deemed safe for consumer use and are subject to fewer regulatory restrictions compared to other items listed on the CCL.
No License Required: Exporters can ship most EAR99 products without the need for an export license. This streamlined process saves time and resources, eliminating the complexities associated with license applications.
Expedited Shipping: Once EAR99 products clear routine screenings, they typically undergo minimal regulatory scrutiny during the shipping process. This translates to faster shipping times, enhancing efficiency in export operations.
EAR99 Licensing Requirements and Exceptions
While EAR99 products generally do not require an export license, there are important exceptions to be aware of:
Embargoed Countries: Exporting EAR99 products to countries under US embargo requires a special license. These countries are subject to trade restrictions due to political or security concerns.
Prohibited End-Users: Exporters must obtain a license if the intended recipient of the EAR99 product is deemed dangerous or prohibited. This ensures that sensitive technology or goods do not fall into the wrong hands.
Illegal Use: If there is evidence or suspicion that the product will be used for illegal activities, such as terrorism or human rights violations, an export license is necessary to prevent unauthorized export.
These exceptions are crucial for compliance with export regulations and ensuring that EAR99 products are exported responsibly and legally.
EAR99 Products: Examples and Categories
EAR99 products include a wide range of low-tech consumer goods and services that do not fall under other restricted lists. Some common examples include:
- Packaged Food: Non-perishable food items packaged for retail sale, such as snacks, canned goods, and packaged beverages.
- Stationery Items: Basic office supplies like pens, pencils, notebooks, and paper products used for writing, drawing, or organizing.
- Household Goods: Everyday items used in homes, including kitchenware, cleaning supplies, home decor, and small appliances.
- Daily-Use Electronics: Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, headphones, and accessories like chargers and cables.
- Clothing Items: Apparel for daily wear, including shirts, pants, dresses, outerwear, and accessories like hats, scarves, and gloves.
- Footwear: Various types of shoes for different purposes, including sneakers, sandals, boots, and slippers.
These examples demonstrate the diverse nature of EAR99 products, which play a significant role in international trade and commerce. Understanding the categories helps exporters navigate regulations and compliance requirements more effectively.
How to Determine if Your Product Falls Under EAR99 Category?
Finding the EAR99 classification for your product is crucial for smooth export operations. While EAR99 products don’t have specific numbers assigned to them, you can follow these steps to verify if your product belongs to this category:
Step 1: Identify Product Category
Begin by thoroughly examining your product’s details to determine its category. Review its specifications and intended use to ascertain whether it aligns with any categories listed in the Commerce Control List (CCL).
Step 2: Check Commerce Control List (CCL)
Consult the CCL to see if your product is explicitly listed within its categories. If you don’t find your product listed, it is likely classified as EAR99. EAR99 items typically encompass low-tech consumer goods and services not covered by other export control classifications.
For instance, suppose you’re exporting clothing items from the US. To confirm EAR99 classification, ensure the clothing is suitable for consumer use. Then, verify that the product is absent from the CCL. Finally, ensure compliance by avoiding exports to restricted countries and illegal activities. Understanding these steps facilitates seamless navigation of export regulations and compliance obligations.
When Does EAR99 Apply?
Determining when EAR99 classification applies is essential for exporters navigating trade regulations. Here’s a breakdown of the conditions under which EAR99 applies:
Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) Jurisdiction
EAR99 classification falls under the jurisdiction of the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS), a branch of the U.S. Department of Commerce. Products classified as EAR99 are subject to BIS regulations.
Exclusion from Commerce Control List (CCL)
EAR99 applies to products that are not listed in the Commerce Control List (CCL). These items are typically low-tech consumer goods and services that do not fall under specific export control classifications.
No License Required (NLR) Status
Products classified as EAR99 are granted a No License Required (NLR) status, meaning exporters do not need to obtain an export license for their shipment.
Conditions for EAR99 Classification
For a product to be classified as EAR99, it must meet the following conditions:
- Exclusion from International Traffic in Arms Regulation (ITAR): The item is not subject to the regulations outlined in the International Traffic in Arms Regulation (ITAR), which governs the export and import of defense-related articles and services.
- Absence of Other Federal Agency Regulations: The product is not subject to export regulations enforced by any other federal agency besides the BIS.
- Not Listed on the CCL: The item is not listed in the Commerce Control List, indicating that it is not subject to specific export control classifications or restrictions.
These conditions help exporters determine the appropriate classification for their products and ensures compliance with export regulations.
EAR99 vs ITAR vs ECCN vs NLR
This table below gives you a comprehensive overview of the differences between EAR99, ITAR, ECCN, and NLR, covering various aspects including regulation authority, scope, licensing requirements, enforcement authority, and documentation required.
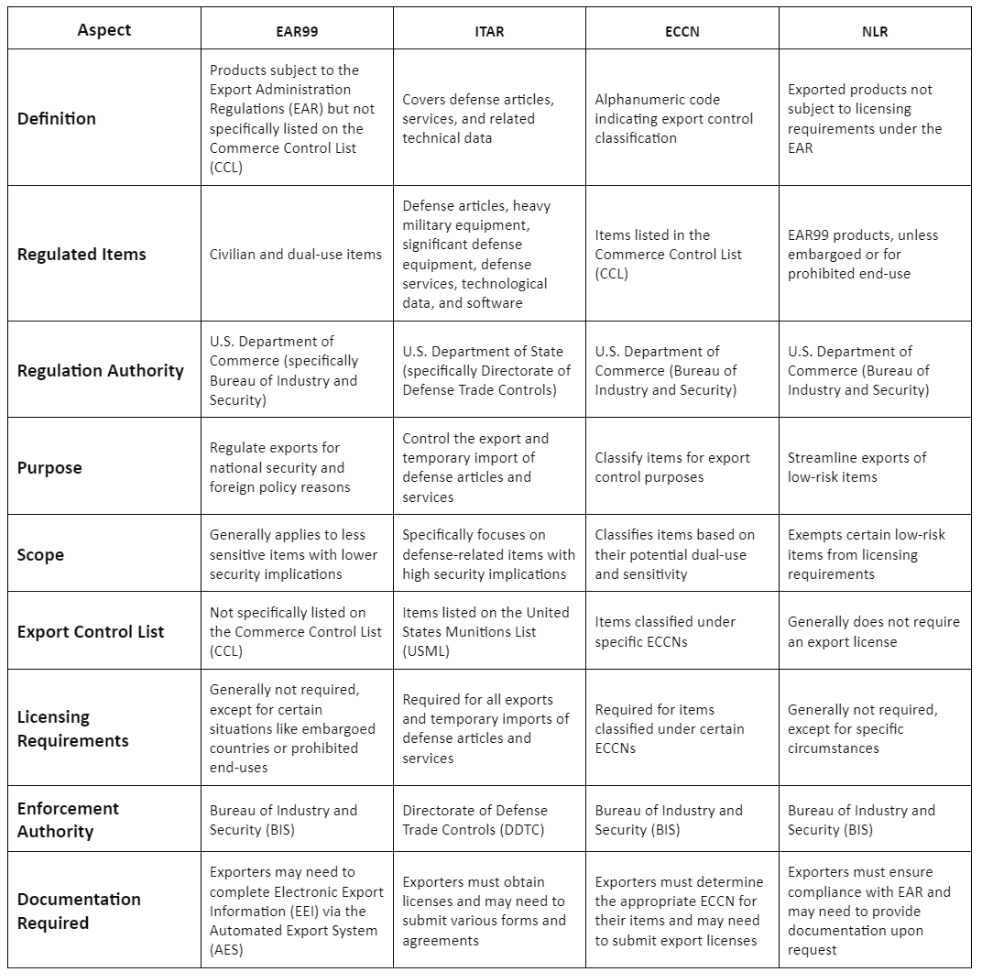
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between EAR99, ITAR, ECCN, and NLR is essential for navigating the complex landscape of export regulations. While EAR99 offers flexibility for exporting low-tech consumer goods and services, compliance with export laws remains paramount to prevent unauthorized exports and maintain national security interests. With streamlined processes and fewer regulatory restrictions, EAR99 products play a significant role in facilitating international trade while ensuring responsible and lawful export practices.
Also Read: Top 5 Ways To Finance Your International Trade/Export Business in 2024
In the dynamic world of business, managing finances efficiently is key to ensuring sustained growth and success. One crucial aspect that often takes center stage is the management of receivables – the money owed to your business by customers.
This blog aims to shed light on the strategic use of financing receivables and the impactful practice of vendor financing, offering insights that are both accessible and beneficial to businesses of all sizes.
Financing Receivables:- What is Financing Receivables

Accounts receivable financing is a different way to get money compared to going to a regular bank. Basically, it’s a money move where you borrow cash using the money your customers owe you.
Here’s the deal: if your company is waiting for money to come in, but you need cash ASAP to cover your bills, accounts receivable financing steps in to help. It’s also great for businesses that don’t want to hassle with collecting money from people who owe them. Instead, they can pay a little fee and get the money right away.
In simple terms, it’s like turning the future money you’re expecting into real cash when you need it!
Types of Financing Receivables
Here are different types of financing receivables options that you need to understand:
Collateralized Loan Option
- If you have customers who owe you money, you can use these accounts as collateral for a loan from a financing company.
- When your customers settle their bills, you can use that money to pay off the loan.
Invoice Factoring Option
- Another way is to sell your accounts receivable to a factoring company.
- With a service known as invoice factoring, the factoring company buys your non-delinquent unpaid invoices.
- They pay you an upfront percentage, called the advance rate, of what your customers owe.
- The factoring company then collects payments directly from your customers, and once the accounts receivable are paid, they keep a small factoring fee and give you the remaining balance.
Advantages of Financing Receivables
Understand some of the benefits of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Upfront Cash for Unpaid Accounts: With receivables financing, you receive immediate funds for invoices that your customers haven’t paid yet. It’s like getting a cash advance based on the money you’re expecting to receive in the future.
Potentially Lower Financing Costs: The financing rate in receivables financing may be more cost-effective compared to other borrowing options such as traditional loans or lines of credit. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to manage their costs while accessing the necessary funds.
Relief from Unpaid Bill Collection: Opting for receivables financing can lift the weight of chasing down unpaid bills from your shoulders. Instead of spending time and resources on collections, a financing company takes on this task. It allows your business to focus on its core activities while ensuring a steady flow of working capital.
Ideal for Cash Flow Challenges: Receivables financing is a great solution for businesses facing cash flow issues. Whether you’re waiting for payments from customers or need quick funds to cover operational expenses, this option provides a flexible and accessible way to address cash flow gaps. It’s suitable for a variety of companies, regardless of their size or industry, offering a lifeline during financially challenging periods.
Disadvantages of Financing Receivables
Understand some of the cons of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Requirement of Outstanding Invoices: To benefit from receivable financing, your business must have outstanding invoices, meaning customers owe you money. This financial option leverages these accounts receivable as assets that can be used to secure a loan or sell to a factoring company.
Importance of Clear Terms for Unpaid Accounts: Keeping clear and accurate records of the terms associated with unpaid accounts is crucial. This includes documenting when payments are expected, the amounts owed, and any specific conditions. Maintaining meticulous records is essential for the smooth process of receivable financing, ensuring transparency and accuracy in the transactions.
Impact of Credit History on Qualification: Qualifying for receivable financing may depend on your business’s credit history. If your business lacks a stable credit history, it could pose a challenge in accessing this form of financing. Lenders or factoring companies often assess the creditworthiness of a business before extending receivable financing. Having a stable credit history enhances your eligibility and may lead to more favorable terms. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining good financial standing to maximize the benefits of receivable financing.
Vendor Financing:- What is Vendor Financing?

Vendor financing, also known as supplier financing or trade credit, is a financial arrangement where a company obtains funding or extended payment terms from its suppliers. In this scenario, the vendor, or the supplier of goods or services, plays a crucial role in providing financial support to the purchasing company.
It’s a smart move when you’re buying a lot of big stuff. If you’re getting things like inventory for a store, computers, vehicles, or machinery, talk to your suppliers about financing deals. It’s like making a deal to pay for these things over time instead of all at once. This helps you avoid running low on cash and gives you the chance to grow your business while paying for the equipment. It’s a win-win!
Also Read : What Is a Vendor? Definition, Types, and Example
Benefits of Vendor Financing
Understand some of the benefits of vendor financing to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Equipment Purchase without Upfront Payment: One big advantage of vendor financing is that it lets you buy the equipment you need without having to pay for it all upfront. Instead of emptying your wallet in one go, you can work out a deal with your vendor to spread the cost over time. This means you can get essential equipment for your business without a hefty immediate expense.
Preservation of Cash for Emergencies: By using vendor financing, you’re able to keep more cash on hand. This is crucial for dealing with unexpected emergencies or opportunities that may come up in your business journey. Preserving your cash flow provides a financial safety net, allowing you to handle unforeseen challenges without disrupting your day-to-day operations or long-term plans.
Also Read: How to Use Vendor Financing to Buy a Business?
Disadvantages of Vendor Financing
Understand some of the cons of financing receivables to help you make a wiser and informed decision:
Extended Payment Period: One downside of vendor financing is that your payments might stretch out over a long period. While this eases the immediate financial burden, it could mean you’re committed to paying for the equipment over an extended timeframe. This extended payment period may limit your financial flexibility and tie up resources that could be used for other business needs.
Risk of Equipment Retrieval: If you fall behind on your payments, there’s a risk that the vendor could take back the equipment. This is a significant concern because it means not keeping up with your agreed-upon payment schedule could result in losing the very equipment your business relies on. It emphasizes the importance of carefully managing your financial commitments to avoid potential disruptions to your operations.
Distinguishing Accounts Receivables Finance from Accounts Receivable Factoring
Navigating the world of turning accounts receivables into immediate cash flow can be a game-changer for businesses in need of quick funds. While both services share the common goal of providing timely financial solutions, it’s essential to understand their fundamental differences:
Nature of the Transactions
Accounts Receivables Finance (Invoice Financing)
Think of this as a loan. Your business uses its outstanding invoices as collateral to secure a loan. It’s a financial arrangement where you borrow against the money your customers owe you, providing a flexible solution to bridge financial gaps.
Accounts Receivable Factoring
In contrast, factoring involves the outright sale of your receivables. Factoring companies become the owners of the current asset – your unpaid invoices. They pay you a portion upfront (known as the advance), and then they collect the full amount directly from your customers.
Roles of the Service Providers
Factoring Companies
Factoring companies act as buyers of a business’s current assets, taking ownership of the accounts receivable. They assume the responsibility of collecting payments from your customers.
Accounts Receivable Financing Companies
On the other hand, companies providing accounts receivable financing act as financiers or lenders. They extend a loan to your business, using the outstanding invoices as collateral, without taking ownership of the receivables.
Scope of Application
Accounts Receivable Factoring
Factoring is specifically tailored for commercial financing. It is a solution designed for businesses looking to optimize their cash flow by selling their unpaid invoices in commercial transactions.
Final Words
In the world of business, managing finances wisely is the key to success. Whether it’s unlocking cash through accounts receivables financing or securing equipment with vendor financing, these financial tools offer both opportunities and considerations. Accounts receivables financing turns future money into immediate cash, ideal for addressing cash flow challenges.
Vendor financing, on the other hand, lets you spread the cost of essential equipment, preserving cash for emergencies. While each has its advantages, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons. Whether you’re considering accounts receivables financing or vendor financing, understanding these financial strategies empowers you to make informed decisions, propelling your business toward sustained growth and financial resilience.
Credlix is becoming a big player in helping businesses with money. We want to make small businesses stronger, so we offer really good financing solutions made just for them.
Also Read : What Is a Vendor? Definition, Types, and Example
